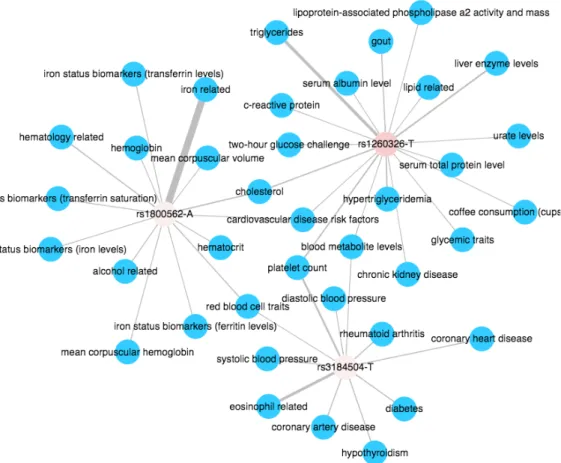
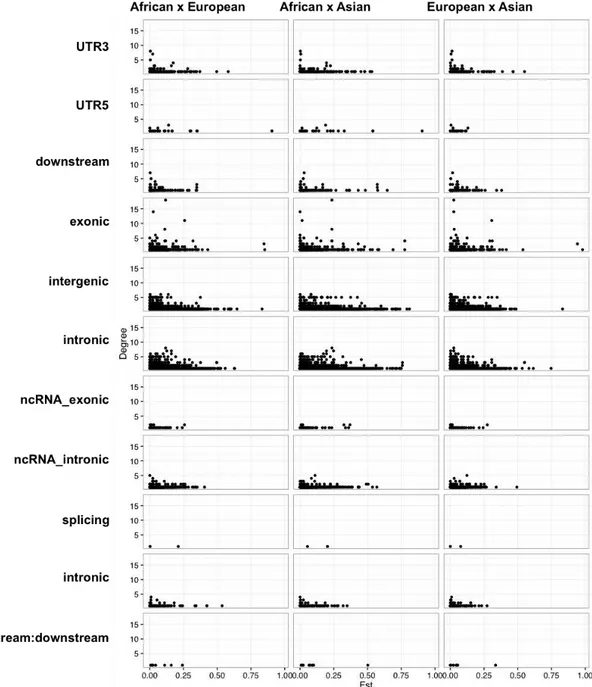
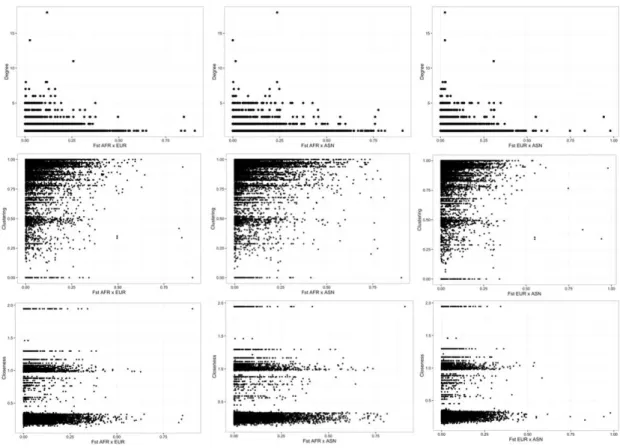
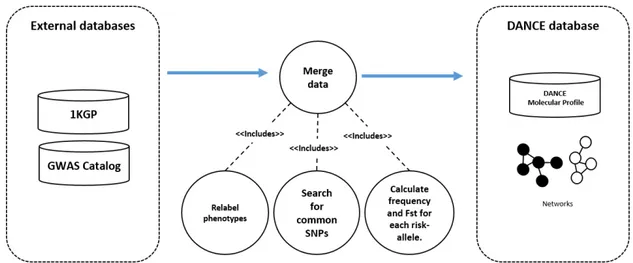
Network-based Methods for Analyzing the Genetics of Human Complex Diseases
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Propôs identificar e analisar se as licenciaturas a distância ofertadas pela Universidade de Brasília (UnB) alteraram o modelo de transferência da informação
The increasingly complex conditions of human populations’ exposure and tolerance to the emergence and resurgence of pathogens and infectious diseases in the global context and
Por certo, as mobilizações indígenas têm contribuído para modificar a imagem de uma América Latina que não está de acordo com a pretensa uniformidade que outrora foi pensada para
The objective of our study was to describe the presence of sexual dysfunction and possible associated comorbidities in a population with chronic neurological diseases, and relate
Methods: We analyzed the mortality due to ischemic heart diseases (IHD), cerebrovascular diseases (CbVD) and external causes (EC) in the population of the metropolitan region of
The present study identified the presence of risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in parents of children with heart diseases, namely obesity, sedentary lifestyle and
In order to establish the insecticide susceptibility status for Anopheles darlingi in Colombia, and as part of the National Network on Insecticide Resistance Surveillance,
The direction of this effect is totally compati- ble with the changes in allele frequencies observed here, since in the present study a high frequency of alleles 1 (D4RAT59) and