Geometrical and optical parameters of Tropopause Cirrus Clouds in the Southern Hemisphere
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
The particle backscatter coefficients were multiplied with the most appropriate lidar ratio, which is given by the Raman lidar observations of extinction and backscatter coefficient
The main objective is to study the extensive (backscatter and extinction coefficients) and intensive (lidar ratio, Ångström exponents) optical properties of free-tropospheric
The height ranges of smoke layers are additionally denoted in Table 1 along with the lidar derived optical parameters for the specific layers, namely the AOD, the mean lidar ratio
Interestingly, an aqueous solution containing NaCl indeed accelerated both the acylhydrazone and oxime formation reactions in a salt con- centration-dependent manner, which corroborates
The investigation of the optical constants such as refractive index, extinction coefficient and dielectric constant of the 3- amino-7-dimethylamino-2-methyl
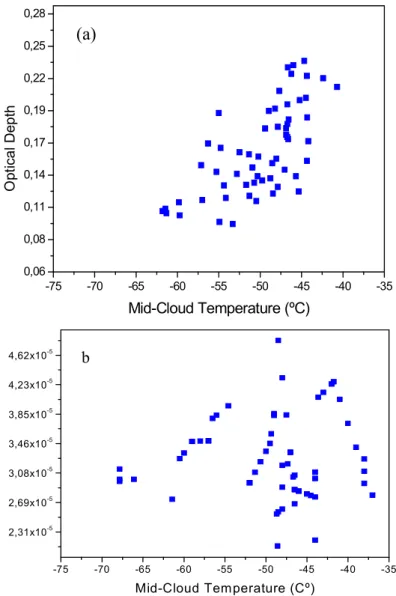
Most of the cirrus clouds appear to be located in the troposphere below the dynamical tropopause even when the cloud top.. is close to the
We correlate the monthly mean aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 670 nm to the monthly mean surface extinction and the fraction of observations where the visibility is below 1– 10
If cirrus clouds lead to a warming or cooling thus depends on their macrophysical properties such as the optical thickness of the cloud which is determined by microphysical
PSC microphysical properties were retrieved by comparison of the measured particle depolarization ratio and PSC-averaged lidar ratio to theoretical optical data obtained for