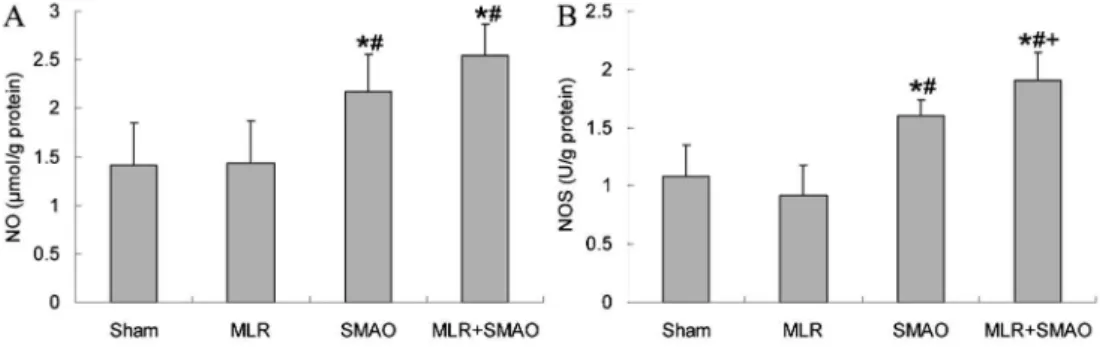
Mesenteric lymph reperfusion exacerbates spleen injury caused by superior mesenteric artery occlusion shock
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
NaHS administration significantly enhanced IL-10 (P , 0.01) and IL-12 (P , 0.05) levels compared to the shock+ +drainage group, as well as with significant differences compared to
The intestinal ischemia/reperfusion group received 45 min of superior mesenteric artery occlusion, while the ischemic preconditioning group received 10 min of short ischemia
Monografia (Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso de Pós Graduação em Engenharia de Segurança no Trabalho). Universidade Estadual de Ponta Grossa. COMPANHIA ENERGÉTICA DE
artery; Ischemia and reperfusion group (IRG, n=10): clamping of superior mesenteric vessels plus saline solution; Ischemia and reperfusion plus Atenolol group (IRG+At,
Ten rats underwent intestinal ischemia for 30 minutes by occlusion of the cranial mesenteric artery with a vascular clamp, followed by reperfusion for 60 minutes for removal of the
• Group A - I/R: comprised of ten rats subjected to intestinal ischemia by occlusion of the cranial mesenteric artery with a vascular clamp for 30 minutes, followed by reperfusion
Macro specimen (female, 61 years). 1) inferior mesenteric artery; 2) superior mesenteric artery; 3) common trunk of the right colic and middle colic arteries; 4) common trunk of
In the present work, we describe an endothelium-dependent vasodilator effect of HSE in superior mesenteric artery rings of rats, through a mechanism dependent on release of nitric