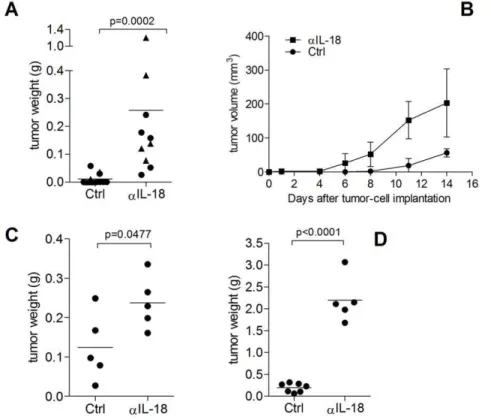
IL-18 inhibits growth of murine orthotopic prostate carcinomas via both adaptive and innate immune mechanisms.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Conclusion: The results indicate that genistein inhibits growth of the hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells, LNCaP, via apoptosis induction through regulation of
Taken together, these results suggest that IL-27 enhances the expression of TRAIL and TLR3 in human melanomas and inhibits their tumor growth in cooperation with poly(I:C), partly in
The canonical effector mechanisms mediated by caspase-1 are the maturation and secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 and the induction of pyroptosis, a pro-inflammatory form of cell
Työmarkkinoiden kansainvälistymispalveluiden alueellisen kehit- tämisen kohdalla erityisesti arkkitehtuuri-innovaatio tarjoaa kiin- nostavan näkökulman, koska aluekehittäjien
In vitro , STGC3 inhibits the growth of CNE2 cells and suppresses the anchorage-independent growth of these cells in soft agar, implying a tumor-suppressor role for this Figure 3
Moreover, the mRNA (Figure 7B) and protein (Figure 7C and D) expression of NLRP3, IL-1 b , and IL-18 in TGs from trigeminal neuropathic pain mice were significantly inhib- ited
Thus, in this study, we evaluated the roles of GATA-2 in LPS-induced il-1β gene expression and the possible mechanisms using murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells and primary
In the present study, we have shown that IL-1a, IL-1b and IL-18 were released by NHBE cells following HRV14 infection, and that endogenous IL-1 signaling was essential for the
IL-37 markedly reduced NLRP3-dependent neutrophil recruitment and steady state mRNA levels of IL-1 b production and mitigated lung inflammation and damage in a relevant clinical