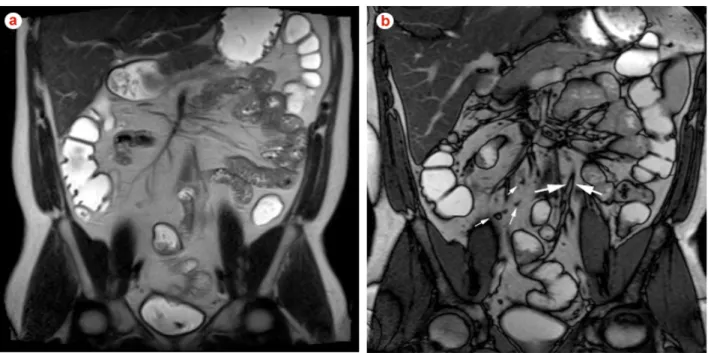
Magnetic resonance imaging of small bowel crohn’s disease
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
In fl ammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn ’ s disease (CD), is associated with low bone mineral density (BMD).. Prevalence of osteope- nia
Magnetic resonance imaging: dynamic contrast enhancement and diffusion-weighted imaging to identify malignant cervical lymph nodes..
VlctlonncÚAt dej> bymbolejb.. kòptctA
Purpose: To compare the performance of apparent diffusion coeficient (ADC) measurement obtained with diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in the characterization
Purpose: To determine the incremental beneit of combined endorectal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging, as compared with endorectal MR imaging alone,
Purpose: To determine the role that magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging ind - ings obtained at the time of diagnosis play in the progression of disease
Purpose: To determine the role that magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging ind - ings obtained at the time of diagnosis play in the progression of disease
AD: Alzheimer’s Disease; MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging; DTI: Diffusion Tensor Imaging; TBSS: Tract-Based Spatial Statistics; TMS: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation; FA: