Association between Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients Associação entre resistência à insulina e fatores de risco cardiovascular em pacientes com síndrome dos ovários policísticos
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The objective of this study was to test for a correlation between fasting serum lipid profiles and levels of testosterone, insulin, leptin, and interleukin 1- β (IL-1 β ) and
In the study population, higher mean values for glucose, fasting insulin, total cholesterol, triglycerides and uric acid and lower levels of HDL-c were observed in individuals
CVD, obese children have a cardiovascular risk profile consis- tent with its early development, i.e., significantly higher blood pressure, triglycerides and fasting insulin and
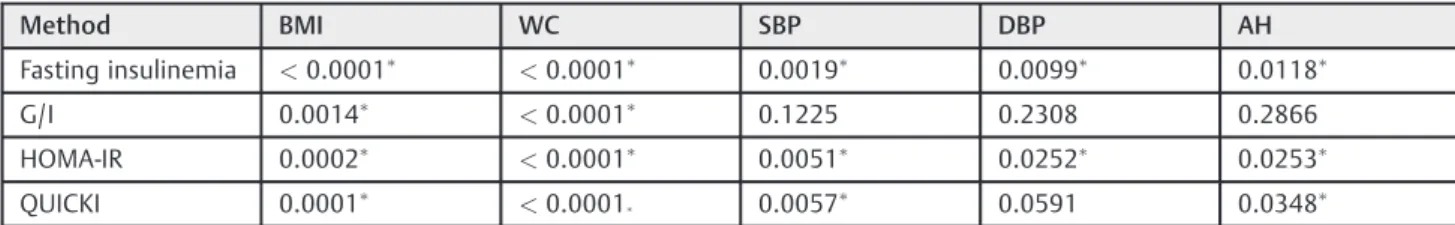
The objective of the present study was to examine to relationship between body mass index and insulin resistance with isolated cardiovascular risk factors and with metabolic
Na relação entre características químicas da madeira e do solo existe uma correlação entre o carbono fixo e o trióxido de enxofre da madeira e grande parte dos
Método: estudo observacional dos casos analíticos de câncer do colo do útero inseridos no Módulo integrador dos registros Hospitalares de câncer e no registro Hospitalar de câncer
Objective: To evaluate the correlation between neck circumference and insulin resistance and components of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with different adiposity levels
Conclusions: The increase in serum uric acid showed a positive statistical correlation with insulin resistance and it is associated with and increased risk of insulin resistance