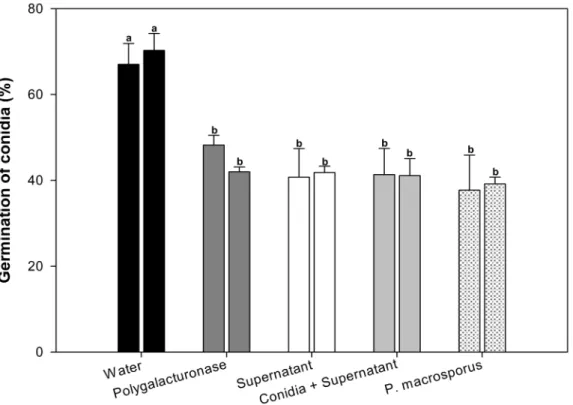
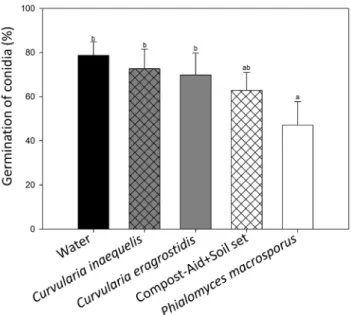
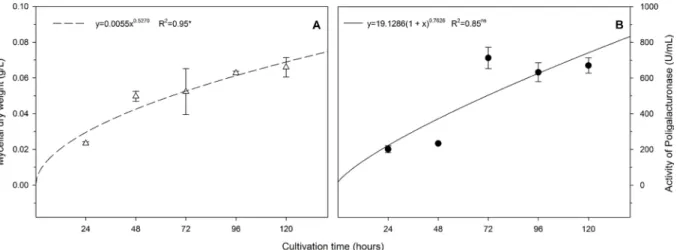
PHIALOMYCES MACROSPORUS REDUCES CERCOSPORA COFFEICOLA SURVIVAL ON SYMPTOMATIC COFFEE LEAVES
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
The best way to achieve this goal is to apply a solvent-free, pH-neutral, hydrophobic adhesive resin layer in a separate step, as confirmed by inferior in vitro and in vivo
We used in vivo and in vitro comet assays to evaluate water samples from three sites on the Paraná River and, in both assays, found an increase in the number of cells dam- aged
Ursolic acid; five lupane type triterpenes: betulin, betulinic acid, lupenone, 3ß-hydroxylup-20(29)-ene-27,28-dioic acid, and 2 α ,3ß-dihydroxylup-20(29)-ene-27,28-dioic acid, and
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the resistance to coffee leaf rust (CLR) caused by Hemileia vastatrix and to Ceratocystis canker (Cc) in coffee genotypes derived
TABLE 4 - Effect of green manures, urea, poultry litter, and Beauveria bassiana on the percentage of healthy coffee berries without Cercospora coffeicola symptoms in
Mode of antiviral activity - To determine the in- hibitory effect of the selected essential oils on DENV replication in vitro , a plaque reduction assay was
triphylla to allow the studies on this extremely rare species and even if appropriate reintroduction in the natural habitat to promote in situ conservation.. triphylla
Therefore, both the additive variance and the deviations of dominance contribute to the estimated gains via selection indexes and for the gains expressed by the progenies