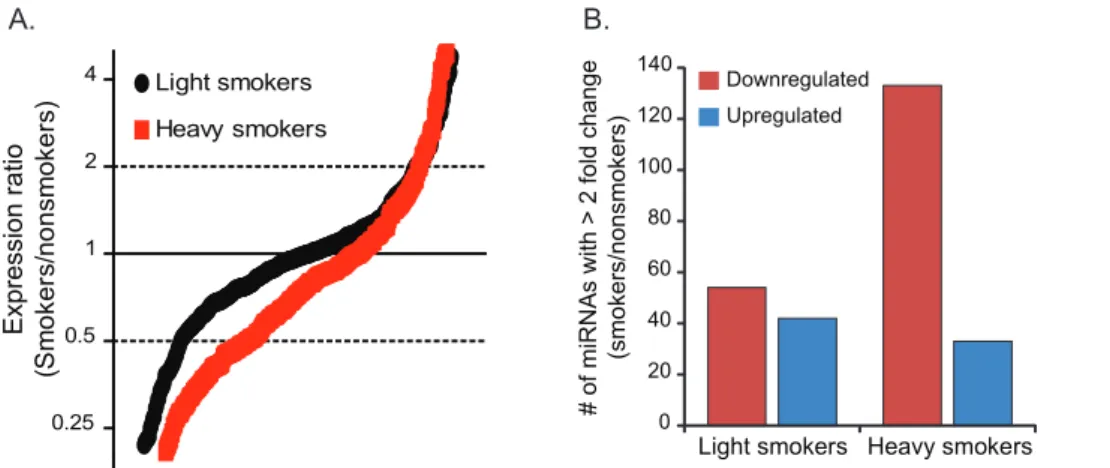
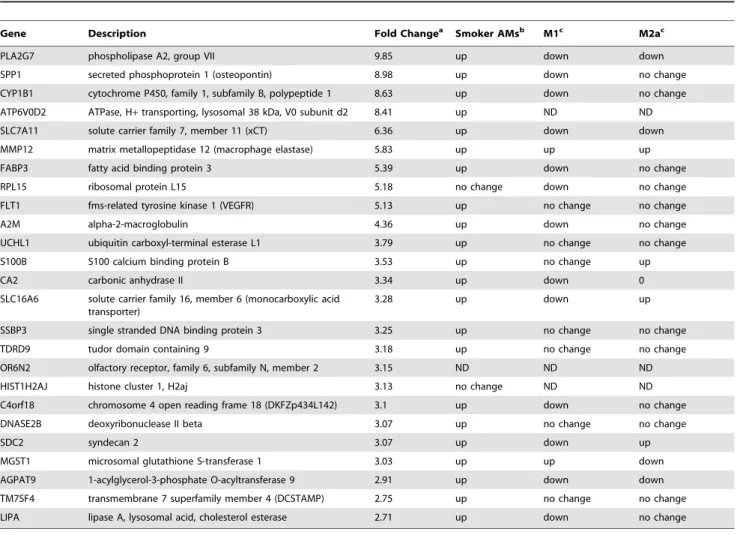
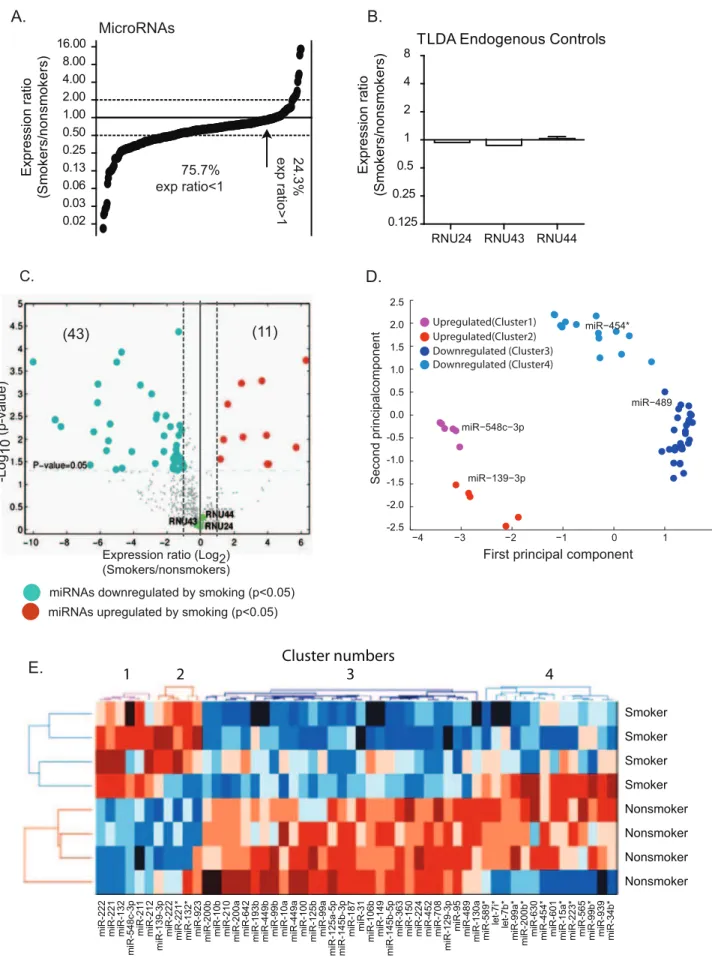
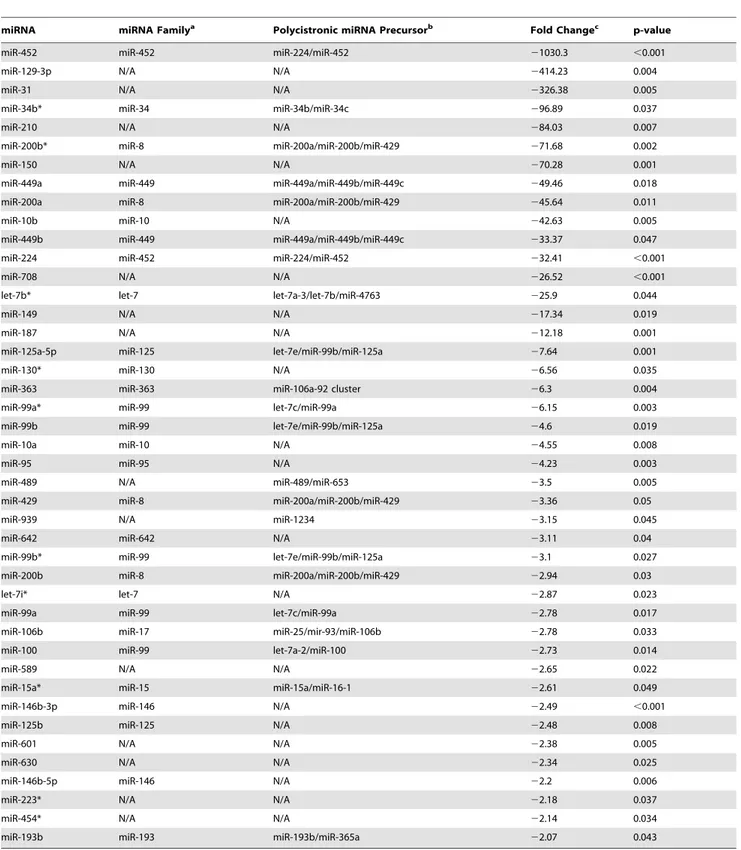
Cigarette smoking decreases global microRNA expression in human alveolar macrophages.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Then, we developed a webtool to allow the analysis of the miRNA genomic context in inter and intragenic regions, the access of miRNA and gene expression data
Furthermore, we investigated a potential correlation between global miRNA abundance and two indicators of kidney function (index of tubulointerstitial injury and level of
Relative expression estimates for the target miRNAs (miRNA-21, miRNA-125b, miRNA-145, and miRNA-630) were obtained by image analysis of the ISH-stained slides ( Table 1 ).The
monocytogenes -induced miRNA expression in primary macrophages, and further analyse the strong effect of D hly-Lm infection on miRNA induction, we quantified changes in miRNA
We have identified 11 putative novel testis- expressed miRNAs in addition to the miRNA variants on the X chromosome described previously [44].. Compared to adult testis
Methodology/Principal Findings: Although miRNA expression levels may not be routinely measured in high-throughput experiments, a possible involvement of miRNAs in the deregulation
Inflorescence miRNome of Orchis italica.. Relative expression pattern of selected conserved and putative novel miRNAs in different tissues of O. The predicted structure of the
The expression of this miRNA had been correlated to the presence of KRAS mutations in colon cancer patients; (2) we used a microarray platform to identify differentially