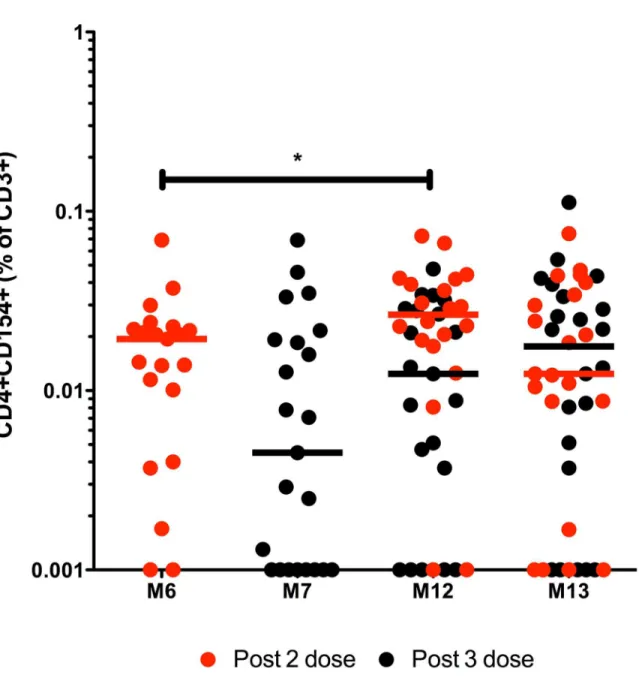
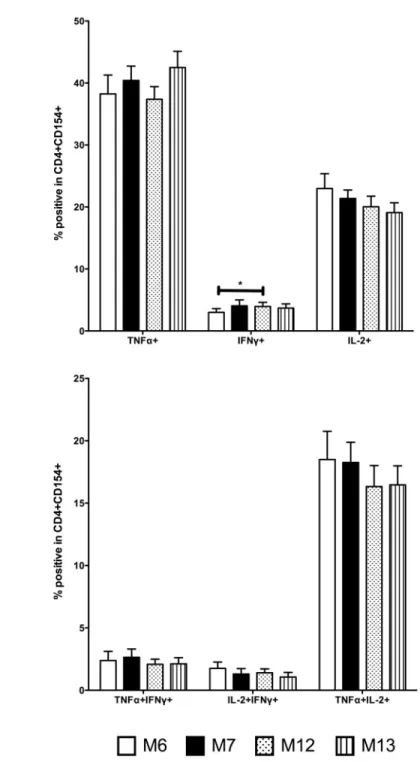
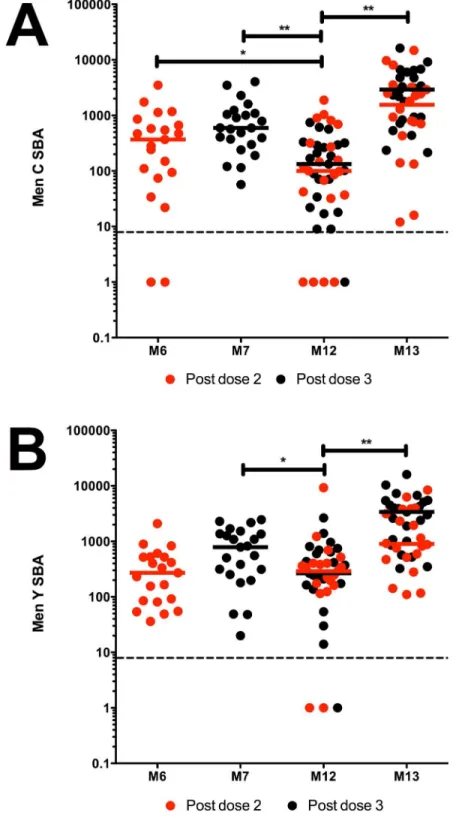
Human Infant Memory B Cell and CD4+ T Cell Responses to HibMenCY-TT Glyco-Conjugate Vaccine.
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
effects of CsA and Tac on the differentiation of naı¨ve CD4 + T cells into cytokine-producing memory T cells as well as on the actual cytokine secretion from memory CD4 + T cells
However, infants who were breastfed until 3 months had higher CD8 T-cell numbers than infants who were never breastfed, and this change persisted when breastfeeding was prolonged
Correlations between cell proliferation (counts per minute) and frequencies of CD5 + , CD4 + and CD8 + T-cells following in vitro peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures derived
Somewhat surprising was the higher activation markers on CD8+ T cells at 12 months and on CD4+ T cells at 6-12 years in HEU compared to the control group.. Other studies have shown
Con- sequently, the objective of our study was to characterize these specific peripheral blood B cell subsets (transitional, naïve, unswitched memory, post-germinal, and resting
The number of circulating MenC-PS-specific IgA memory B cells prior to the booster showed a moderate correlation with the IgA level in saliva at one month and one year post-booster
The acute expansion of a splenic CD4 T cell population expressing CXCR5 and Bcl-6, but not PD-1, was associated with the differentiation of activated memory B cells and production
There was also a greater induction of IFN- c + cells in the B cell gate than in the CD4+ or CD8+ T cell gate (Figure 5D–E) and the percentage of IFN- c + B cells in total