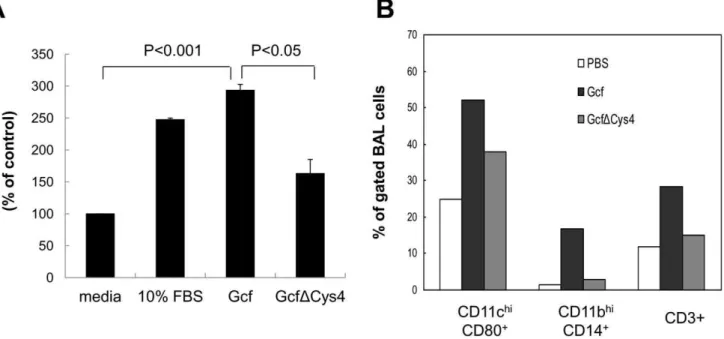
Dual role of respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein fragment as a mucosal immunogen and chemotactic adjuvant.
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Neste sentido, o presente estudo buscou aplicar a análise de agrupamentos para definir oportunidades de redução de custos na rede de distribuição de mel de uma
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis is the most frequent cause of lower respiratory tract illness (LRTI) and hospitalization in young infants worldwide.. 1,2
3: temporal trend of sample positivity (indirect immunofluorescence) for respiratory syncytial virus, hospitalisation rates for RSV-associ- ated bronchiolitis and pneumonia,
respiratory syncytial virus infection in italian infants hospitalized for acute lower respiratory tract infections, and association between respiratory syncytial virus infection
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), one of the most important respiratory viruses, is responsible for annual epidemic ARI outbreaks in infants and pre-scholar children, worldwide
Methods— We analyze the relative burden of influenza, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus and metapneumovirus, their seasonality and their association
Conclusion: Correlation between clinical phenotype and presence of LRV1 was not observed, although the frequency of the virus is two-fold higher in mucosal lesions than that found
Rapid detection of respiratory syncytial virus in nasopharyngeal aspirates by reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction amplification. Detection of respiratory