Arq. Gastroenterol. vol.51 número1
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Em outras espécies com comportamento recalcitrante, também foi verificado que a viabilidade das sementes na pós colheita é influenciada pelo estádio de desenvolvimento
Não encontrou-se o HBV-DNA em soros de pacientes HBsAg negativos, ou com marcadores de infecção passada pelo HBV.. Entretanto, outros estudos referem a presença do HBV-DNA em casos
Thus, the interest in discovering the probable mechanisms by which the hepatitis C virus perpetuates in the liver, and to determine the conditions that predispose for progression
Prevalence of mixed infection by different hepatitis C virus genotypes in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. Evaluation and comparison of different
Infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) affects millions of individuals in the world, resulting in chronic liver disease like chronic hepatitis (CH) and hepatocellular carcinoma
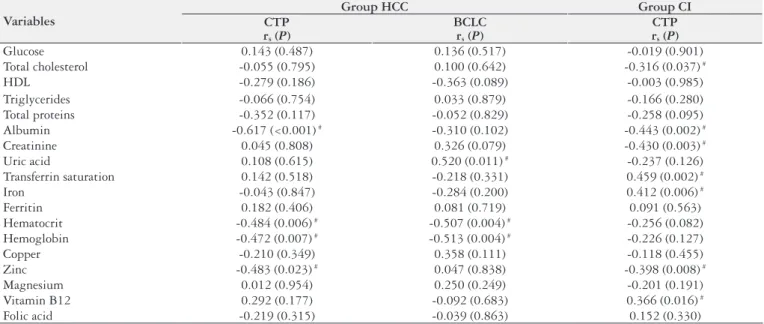
The deterioration of nutritional status seen in patients with cirrhosis is well known (16,18,28,30) , but patients with chronic hepatitis C appear to exhibit more overweight
The patient has no conditions classically associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (virus infection of hepatitis B and hepatitis C, alcoholism,
Only significant p values are shown Helicobacter pylori DNA was found only in the liver of patients with alcoholic hepatitis without cirrhosis, hepatitis B virus (HBV)/hepatitis