Crop rotation, green manure and nitrogen fertilizers in upland rice under no-tillage
Texto
Imagem




Documentos relacionados
Biochar addition did not influence yield components of upland rice and cowpea, but resulted in increased soil N retention, which influenced rice dry shoot mass, spikelets
Plant height (cm), basal stem diameter (mm), leaf area (dm 2 ), shoot dry matter (kg ha -1 ) and leaf nitrogen content (g kg -1 ) of corn plants as a function of hybrid and
The dry matter yield (root, leaf, sheaths and leaf blade) and plant architecture (angle of leaf insertion and leaf arc) were evaluated in rice plants grown in nutrient solutions
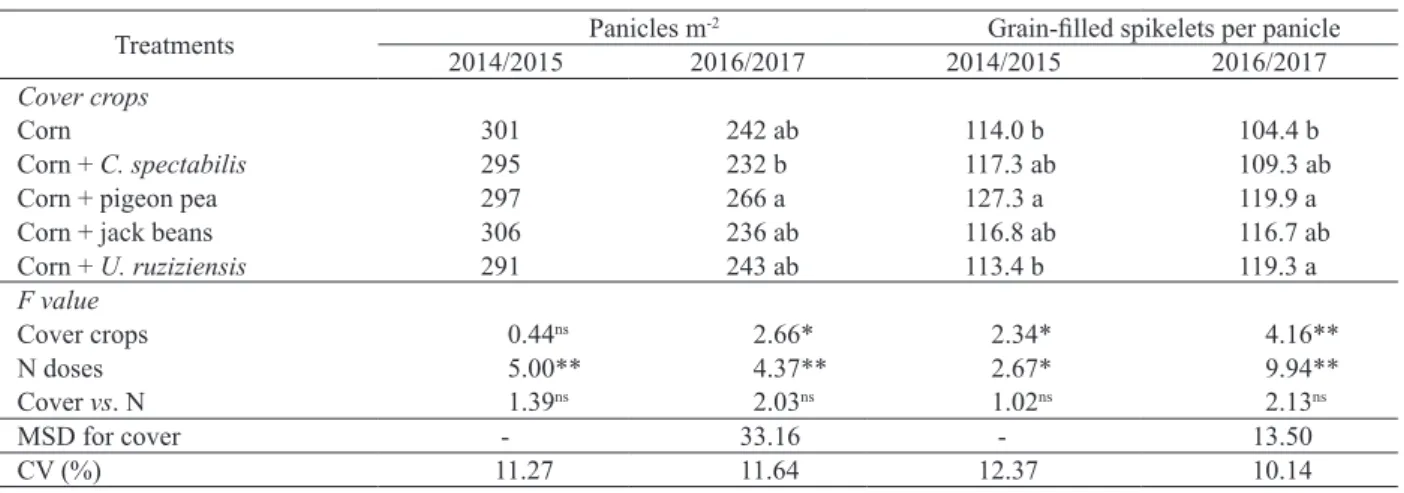
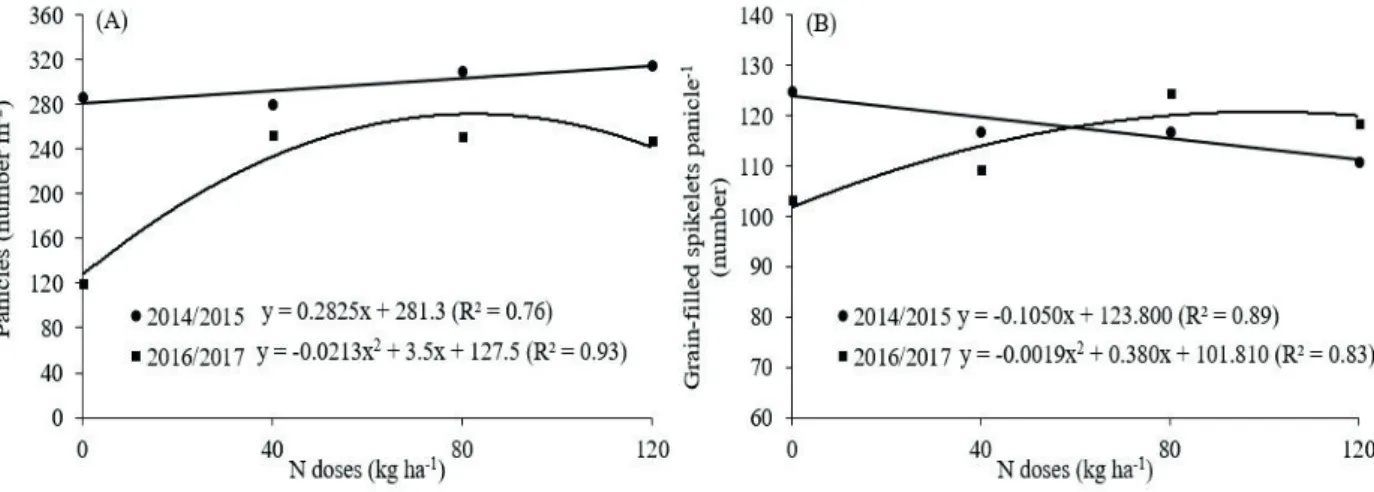
Our data indicate that high grain yields of no-tillage upland rice can be obtained when millet is the preceding cover crop and N applied as nitrate in split rates or the total dose
Surface residue cover after soybean planting in November 2005 was significantly affected by the previous crop, and was highest for sole ruzi grass (Table 5) followed by
stages at PGR application – early tillering phase and panicle primordium differentiation phase – on gas exchange rates, plant height, yield components, and
Predictive accuracy of the GGE biplot models considering the use of the mean phenotypic and genotypic values estimated by the REML/BLUP method for 20 rice genotypes evaluated in
The average natural crossing rate of the upland rice cultivar Guarani to the IAC 201 at a distance of 0.5 m at the environmental conditions of Recife and Carpina counties, state