Long-term nitrogen fertilization in native pasture with Italian ryegrass introduction - Effects on soil health attribute indicators
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Long-term effects of nasal intermittent positive- pressure ventilation on pulmonary function and sleep architecture in patients with neuromuscular diseases. Long
The effects of rhizobial and mycorrhizal inoculation, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on nodulation, mycorrhizal colonization and initial growth were examined in Brazilian
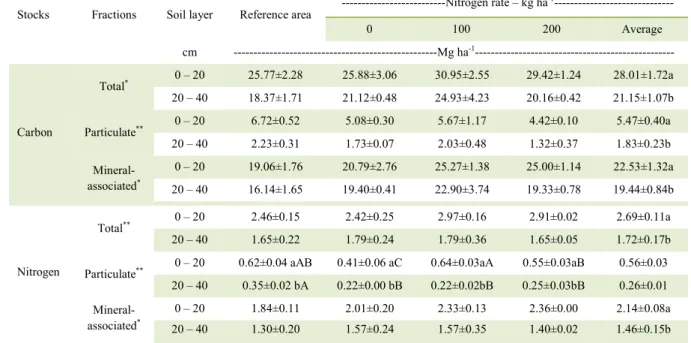
The proce- dures for reclamation improved most of the indicators of soil health in relation to the degraded pasture, such as soil P, mineral N, microbial biomass C,
In the reproductive stage of Italian ryegrass, grazing time, daily number of bites and, feeding stations and time for station are similar between not supplemented and
The bite rate of lambs, on Italian ryegrass plus red clover mixture, under intermittent grazing, was modified in response to changes in sward structure promoted by
This study compared pure and mixed plantations of Eucalyptus grandis and Pseudosamanea guachapele , a N 2 -fixing leguminous tree, in relation.. to their effects on soil C and
Average daily gain, final body weight, body condition score final, final height, weight:height ratio, pelvic area and reproductive tract score of beef heifers fed on ryegrass pasture
The objective of this work was to evaluate the residual and cumulative effects of occasional soil tillage and liming on consolidated NTS, and their interactions with N