Rev. Saúde Pública vol.47 número2
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
In this chapter we explain the secure function evaluation protocol by Lindell and Pinkas [18] which is based on Yao’s work, and also uses the boolean circuit representation..
The general maternal mortality in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, as well as the rates for specific race categories, characterized by a high death risk and deaths related to
Para isso, assumimos, como referencial de análise, as contribuições de Sauvé (2005a), que identifica sete concepções paradigmáticas sobre o ambiente: como
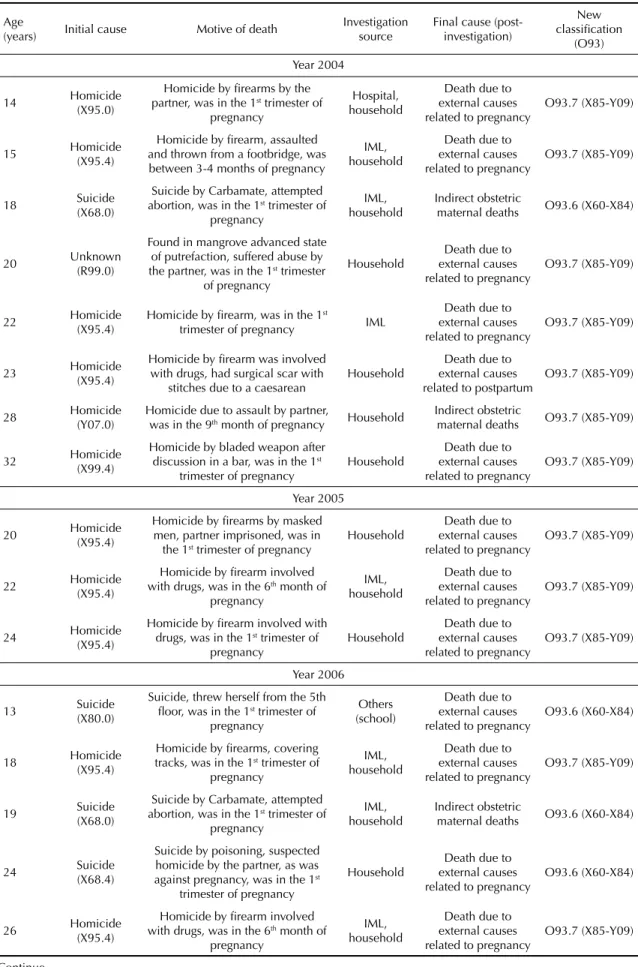
The following tables were developed: historical series of the records of maternal deaths; distribution of sociodemo- graphic aspects and related to pregnancy and childbirth of
Of the variables analyzed, low maternal education, non- white race, multiple gestation, maternal age greater than 35 years old, cesarean delivery, and live female births were
O teste de Duncan, utilizado para diferen- ciar os efeitos ocorridos por tratamento na disponibilidade e matéria seca (Tabela 1), mostra que houve acréscimo quando da intro- dução
To achieve the goal of improved women’s health, Brazil must reach a maternal mortality ratio of no more than 35 deaths per 100 thousand live births, while the forecast for
World Health Organization, who also ind that the main cause of maternal mortality, responsible for one quarter of all maternal deaths, is obstetric hemorrhage that usually