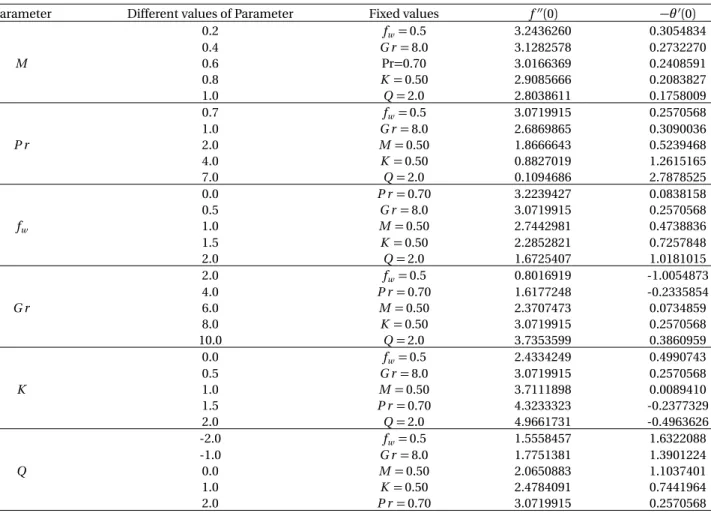
Unsteady MHD free convective heat transfer flow along a vertical porous flat plate with internal heat generation
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Group theory transformation for Soret and Dufour effects on free convective heat and mass transfer with thermophoresis and chemical reaction over a porous stretching surface in
Fig. Homogenized heat transfer coefficient for 10.. 3) For small size of the inclusions a 1 and various values of heat transfer the equivalent heat transfer parameter
Abstract - This work is concerned with the coupled estimation of the heat generated by the reaction (Qr) and the overall heat transfer parameter (UA) during the terpolymerization
(2003) studied the effects of radiation on unsteady free convective flow past a semi-infinite vertical plate with variable surface temperature using Crank-Nicolson finite
Effects of Thermal Radiation and Chemical Reaction on MHD Free Convection Flow past a Flat Plate with Heat Source and Convective Surface Boundary
The thermal mod- els that rely on the known values of the surface temperature, surface heat flow, and surface radiogenic heat generation thus lead to an exponential model for
We consider the flow and heat transfer characteristics of an unsteady, incompressible, viscous and electrically conducting micropolar fluid in a porous channel with expanding
The heat transfer rates decreases with time, Brownian motion parameter, thermophoresis and diffusion-convection parameters whilst it increases with Reynolds number, frequency,