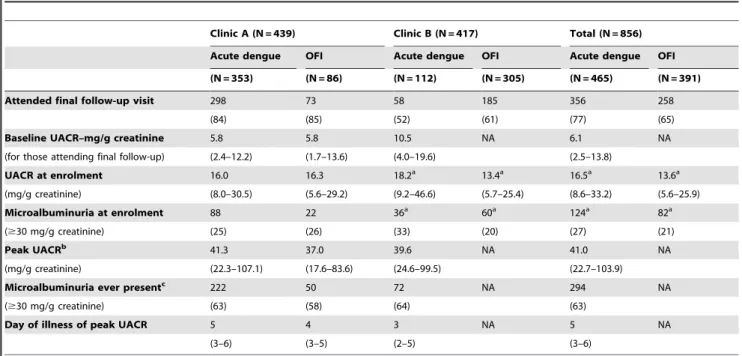
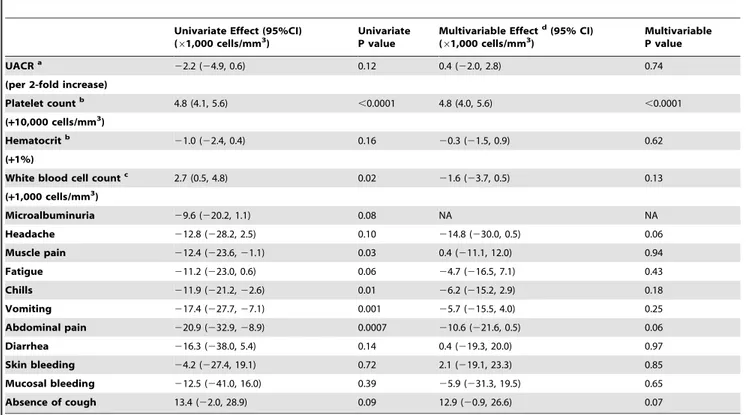
Assessment of microalbuminuria for early diagnosis and risk prediction in dengue infections.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The comparison between age-distributed Zika incidence after the last epidemic in Rio de Janeiro and that of dengue (for the same period and place) is also interesting: the
No statistically significant differences were found between clinical forms, although IL-6 and IFN- J levels were higher in dengue fever cases than in dengue hemorrhagic fever
Methods: Conirmed cases of dengue among city residents during ten years were classiied as dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever, dengue shock syndrome and dengue with
his study in the City of Caxias, Maranhão, showed that although dengue control campaigns emphasize the importance of water containers in the dispersal of the dengue vector,
effusions associated with severe plasma leakage have been described in patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF), but cardiac tamponade is an extremely rare in patients
In addi- tion, seven cases of fatal hemorrhagic disease in adults were reported; one of these cases was confirmed as dengue-1 by virus isolation.. One virologically con-
Despite epidemic dengue activity in Haiti, relatively few cases were confirmed in the Dominican Republic in 1983.. Dengue-4 activity remained high in Trinidad and
In the present study, the variables associated with the progression to persistent symptoms were older age, dengue with warning signs, severe dengue, hospitalization, presence