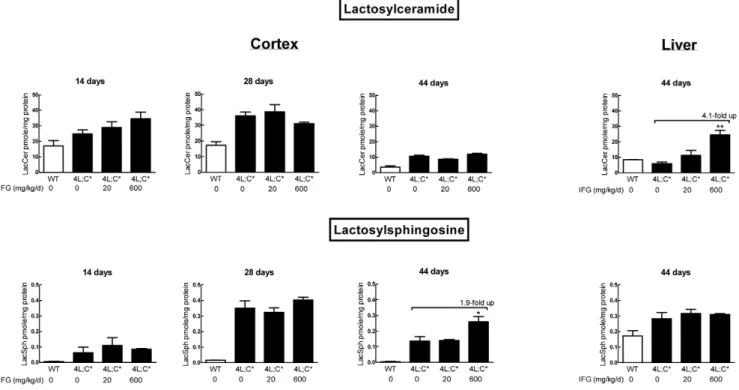
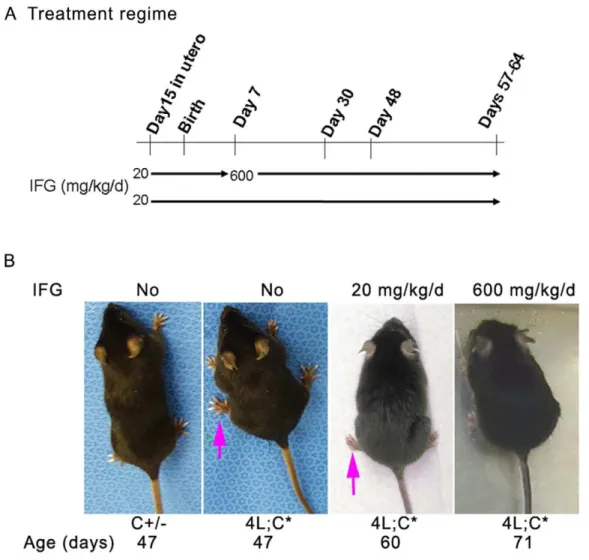
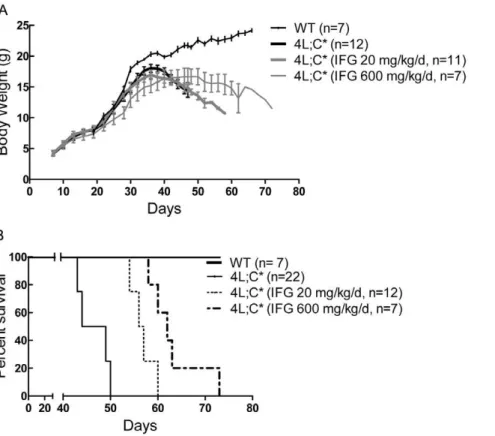
Isofagomine in vivo effects in a neuronopathic Gaucher disease mouse.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
sí mismo (fragmento 48-49) y que la ciencia consiste en el conocimiento de esto último y no de imitaciones, para luego concluir que Aristóteles tuvo que haber defendido en este
Nota- bly, CXCL9 and CXCL10 are chemoattractants, and the recruitment of immune cells to the site of histone injection in a subcutaneous mouse model supports the concept that low
Sendo assim, a presente investigação além de contribuir para a literatura da imagem percebida do Brasil como destino turístico, realizou uma análise comparativa entre
The brain areas involved in the clinical effects of MPH are the same involved in the different mechanisms of chemical dependence, and the increased levels of dopamine found in
To determine if the effects of uroguany- lin in the kidney are mediated by its receptor, GC-C, we employed the sealed-mouse renal function assay on GC-C deficient mice (12)..
-ATPase activity in the synaptic plasma membrane from cere- bral cortex of adult rats submitted to chronic administration of imipramine and fluoxe- tine.. We also studied the in vitro
in the mouse model. TBI also induced an increase in protein expression of COX1, PGE2, and IL-6, as well as a decline in BDNF, PDGF-BB, synapsin-I, and SYP levels. Administration
(54) also demonstrated that the in vivo and in vitro treatment with PTX increased muscle cAMP levels and induced a decrease in the increased rate of total protein degradation in