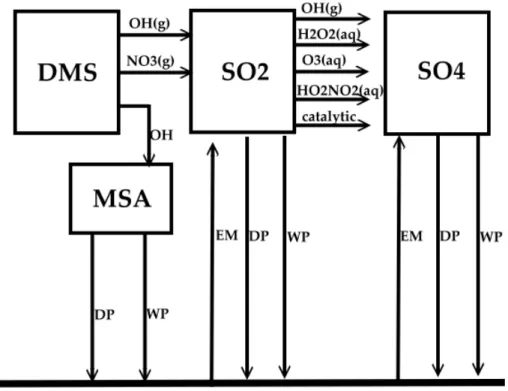
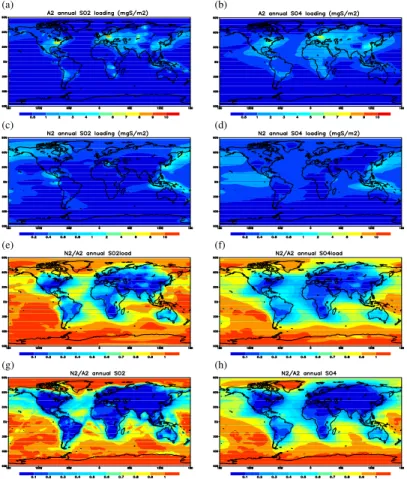
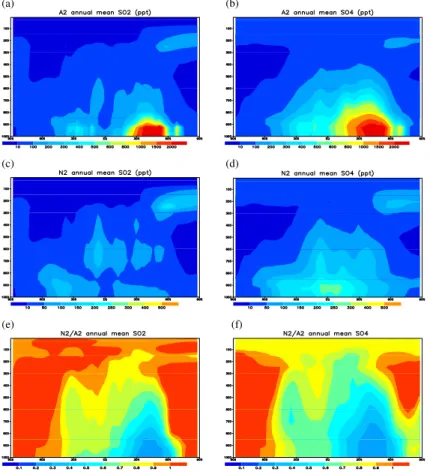
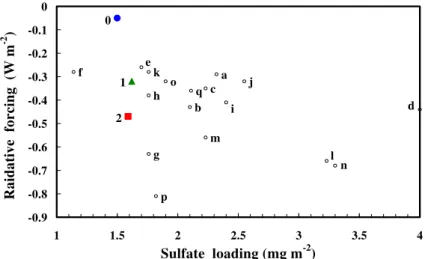
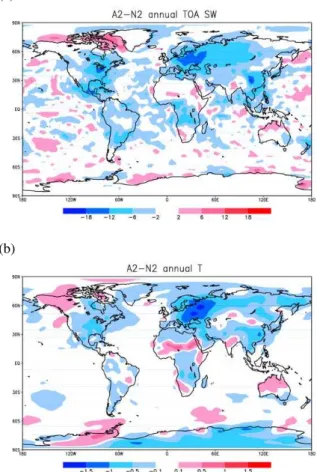
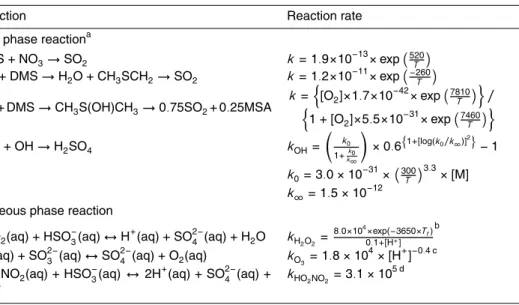
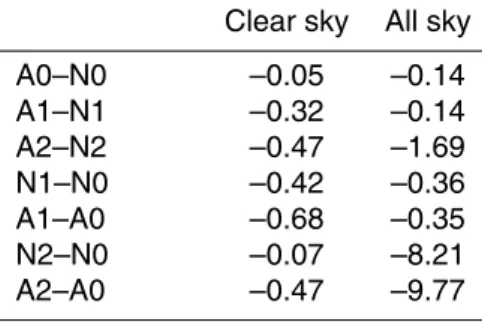
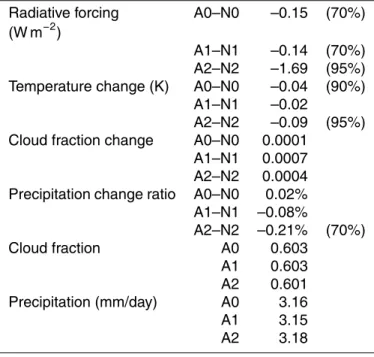
Sulfur cycle and sulfate radiative forcing simulated from a coupled global climate-chemistry model
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Spring 2009, summer 2006 and autumn 2008 concentrations are in a similar range, while val- ues more than twice the median of the other seasons were measured during the high
(2003), in our study the effects of natural processes (in the SFIX sim- ulation) includes also changes in emissions of CO, NO x , and VOCs from biomass burning and lightning
The model has been used to study the impact of aerosol direct radiative e ff ect on East Asian climate (Zhang et al., 2012a), direct radiative forcing of anthropogenic aerosols (Bond
A coupled atmospheric chemistry and climate system model was developed using the modal aerosol version of the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Atmosphere
Chemistry and Physics ACCMIP Special Issue, discussing (1) aerosols and total radia- tive forcing (Shindell et al., 2012), (2) historical and future changes in tropospheric ozone
A coupled atmospheric chemistry and climate sys- tem model was developed using the modal aerosol version of the National Center for Atmospheric Research Commu- nity Atmosphere
Tropospheric chemistry and air quality processes were implemented on-line in the Global Environmental Multiscale model.. The integrated model, GEM-AQ, has been developed as a
Relationship between aerosol number concentration and cloud droplet number concen- tration (CDNC) with (a) showing that the volcanically induced cloud albedo e ff ect is larger