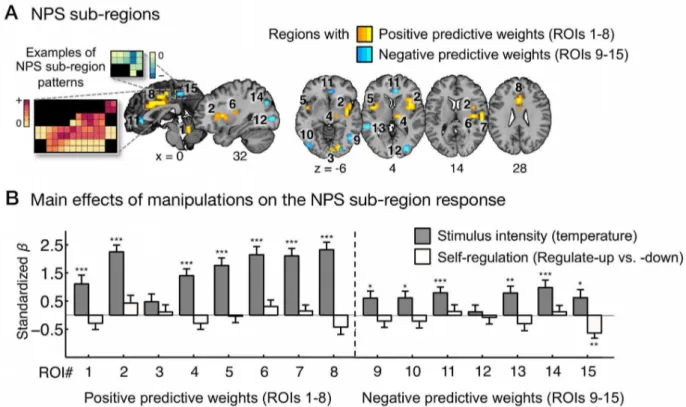
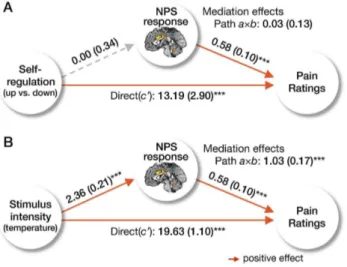
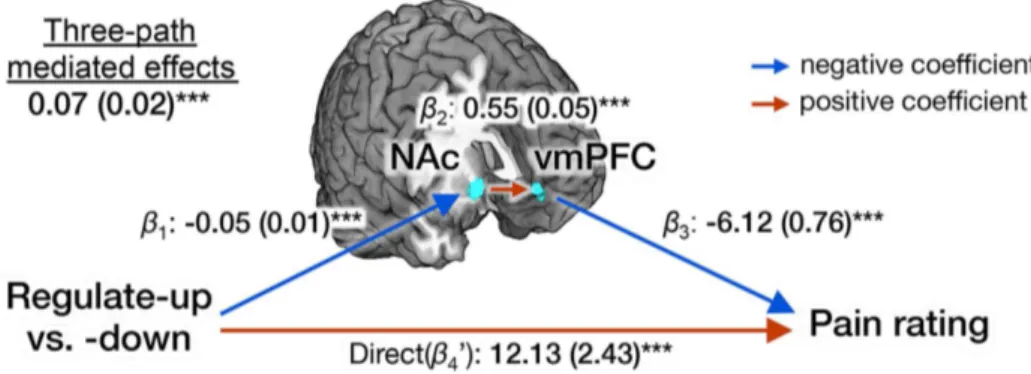
Distinct brain systems mediate the effects of nociceptive input and self-regulation on pain.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Ao realizar o acompanhamento farmacoterapêutico (AFT), o farmacêuti- co assume papel de informante, quanto ao uso correto de medicamentos, ava- lia os riscos a que os pacientes
O consultor deverá informar o cliente, no momento do briefing inicial, de quais as empresas onde não pode efetuar pesquisa do candidato (regra do off-limits). Ou seja, perceber
The probability of attending school four our group of interest in this region increased by 6.5 percentage points after the expansion of the Bolsa Família program in 2007 and
The structure of the remelting zone of the steel C90 steel be- fore conventional tempering consitute cells, dendritic cells, sur- rounded with the cementite, inside of
Follow up with brain CT scan angiography shows focal narrowing of the supraclinoid portion of the left internal carotid artery (curved arrow) and reduction of the flow in the
A própria palavra “virtual” possui certa mobilidade de significado para a autora: na tabela, espaço sonoro real (2.1, real sound-space) relaciona-se com instrumentos
Figure 12 depicts the axial load versus the sum of the fastener forces on the second stud from left to right on the sheathed wall-stud model (see Figure 8(a) for distribution
Involvement of the CA1 orexin 1 receptor (OX1R) on the modulation of orofacial pain and pain-induced changes in hippocampal expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and