Daytime sleepiness in Parkinson's disease: a reappraisal.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
In general, all included studies investigated other sleep variables in addition to daytime sleepiness, such as: sleep duration, sleep quality, sleep hygiene or sleep disorders
The main criteria for diagnosing narcolepsy were the presence of excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, reduced sleep la- tency and presence of sleep-onset REM periods (SOREMP)
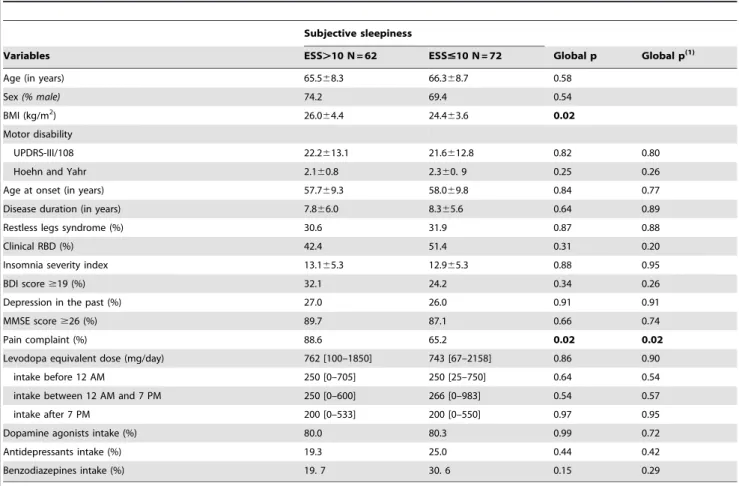
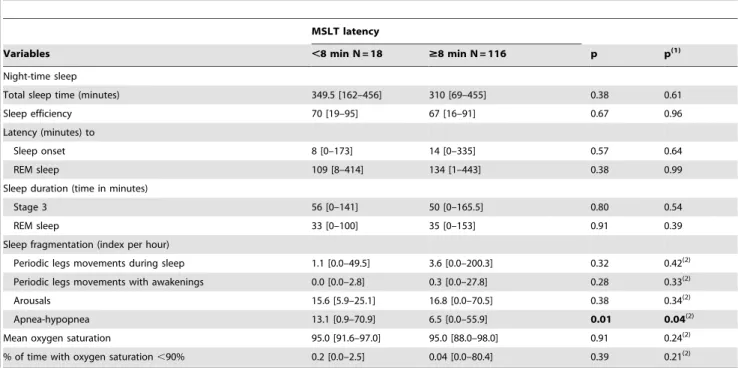
Abstract – Objective: To determine the correlations between excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), assessed by the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS), and the multiple sleep latency
The higher incidence of moderate and severe OSAS explains the high incidence of symptoms indicative of impaired sleep quality and excessive daytime sleepiness (reported in 69%
All patients had symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea (snoring and/or cessation of breath during sleep and/or daytime sleepiness) and underwent diaphragmatic plication via
The objectives of this study were to evaluate clinical characteristics of patients with WUS as compared to gen- eral ischemic stroke, and to further examine the relation- ship
Gender differences in the effect of comorbid insomnia symptom on depression, anxiety, fatigue, and daytime sleepiness in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Kemp
Levels of physical activity were independently associated with exces- sive daytime sleepiness: patients with a sedentary lifestyle developed worse levels of daytime sleepiness