Irritable Bowel Syndrome Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Study.
Texto
Imagem
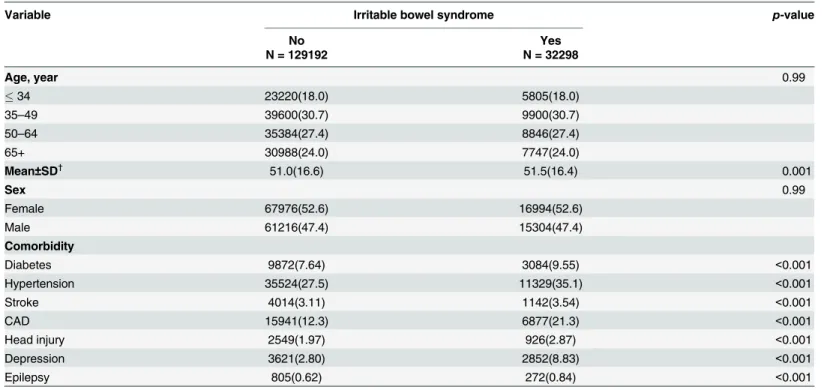



Documentos relacionados
he objective of the present study was to estimate the prevalence of dementia in patients with PD and the efect of risk factors, diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia,
In another study, the relative risk of CRC in patients with CD affecting only the small bowel was similar to the general population, while the relative risk increased to 4.6 and
(BRASIL, 2010) Foram obtidos os resultados apresentados na Tabela 2, acer- ca do peso médio e do teor de princípio ativo para as cápsu- las de fluoxetina. Ao analisar os dados de
The aim of this study was to analyze the data of endoscopy and symptoms in 118 Mexican patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), dyspepsia, non-erosive reflux disease (NERD)
The elevated levels of insulinemia and insulin resistance found in the present study, associated with the higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome, further confirm that patients
Several studies show that the prevalence of overweight/obesity is higher among children from families with higher income In Pelotas, in the 2004 cohort, this prevalence was of
prevalence of dementia in São Paulo city as 12.9%, in the population aged over 60 years, igures equal to or higher than the prevalence rates of dementia found in developed
Risk factors associated with higher prevalence of dementia among illiterates and individuals with low educational level are: low cognitive reserve, poor control of
