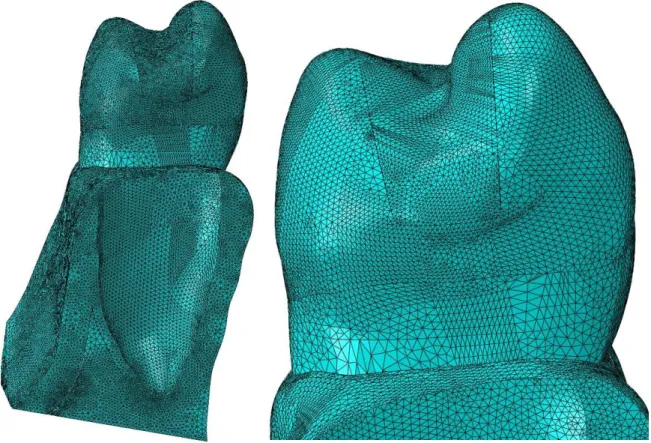
MODELING OF CRACK PROPAGATION IN A PREMOLAR TOOTH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Figure B.2: Storage modulus (E’) and loss modulus (E’’) curves versus temperature, obtained by DMA on a amorphous lactose-trehalose sugar system, hydrated under a a w of 0,00
The direct coating technique involves the deposition of the multilayer film on the surface of single cells or cell aggregates.. The indirect method refers to
Agora, com a reforma da ação executiva, cabe ao AE pôr termo ao processo executivo, sendo efetuada por notificação às partes (exequente, executado e credores reclamantes) 137.
As K decrease from 1 to 0, the tensile stress concentration is obviously around borehole in the vertical direction, and radial cracks grow from the stress
In numerical modeling, the interaction of non-uniform blast loading on the concrete slab was modeled using the incorpo- ration of the finite element method with a crack
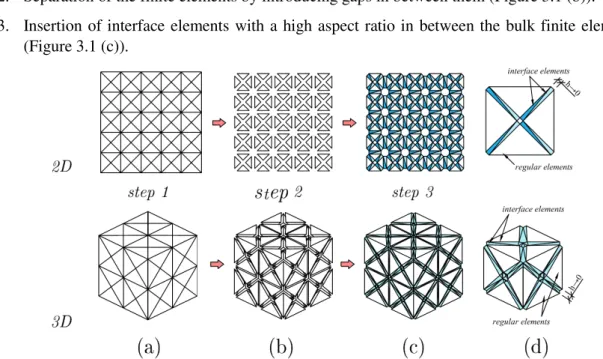
Recently, there has been significant progress in the direction of discrete crack growth modeling – the development of a partition of unity finite element method for crack
Para a equalização da tensão nos dispositivos semicondutores de potência em série, tem- se em conta os regimes estático e dinâmico dos mesmos. O regime estático, acontece
The model simulates a water balance on the canopy and trunks as a function of the climatic parameters R (mean rainfall rate falling on the saturated canopy) and E (mean