Water Erosion in Different Slope Lengths on Bare Soil
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
In 2009, the soil and water losses were higher in the native caatinga plot for the late pattern of rainfall, while in the thinned and natural herbaceous plots the losses were
This research investigated the effects of maize intercropped with jack bean on soil losses due to water erosion, estimate C factor of Universal Soil Losses Equation (USLE) and how
Likely for bare soil, the simulated values did not follow the variation of observed soil moisture contents in the bottom layers, because the model underestimated soil water
The criteria for monitoring A due to water erosion in the Samambaia watershed were determined using the intersection between the following variables: slope, slope
Abstract – The objective of this work was to express soil roughness through statistical, geostatistical, and fractal indexes, comparing and relating them to soil and water losses
ABSTRACT: Among the equations available to describe the relation between matric potential and soil water content, the soil water retention function, the most commonly used is
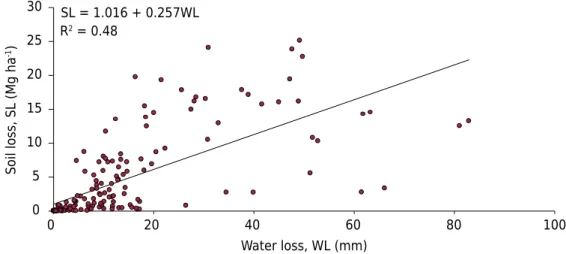
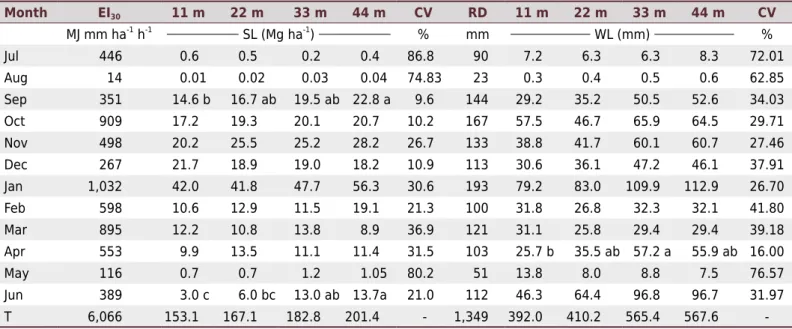
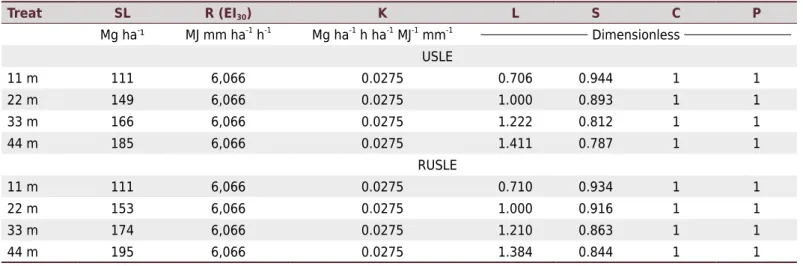
The objective of this study was to quantify the water losses (WL) and soil losses (SL) by water erosion, between the second and third years of eucalyptus ( Eucalyptus benthamii)
The following variables were calculated: rainfall erosivity factor, using the precipitation data; soil erodibility factor, by the correlation between erosivity and soil losses


