Efficient In Vitro Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Mature and Immature Embryos of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The transition from pro-embryogenic cultures to somatic embryo is a critical developmental event affecting the final yield of somatic embryos produced in culture. Thus, a
Table 1 - Effect of different types and concentrations of growth regulators on induction of embryogenic callus and somatic embryos of yacón ( Smallanthus sonchifolius) in the
Shoot apex in induction medium; (b) primary somatic embryos at the globular stage on the explant surface after ten days of culture in induction medium; (c) torpedo
For the first time, a plant regeneration protocol was developed in this study via somatic embryogenesis from leaf and internode derived callus for this species.. This
The use of trichlorophenoxyacetic acid and picloran resulted in a lower percentage of embryogenic callus induction in the RB855156 cultivar, whereas no embryogenic callus
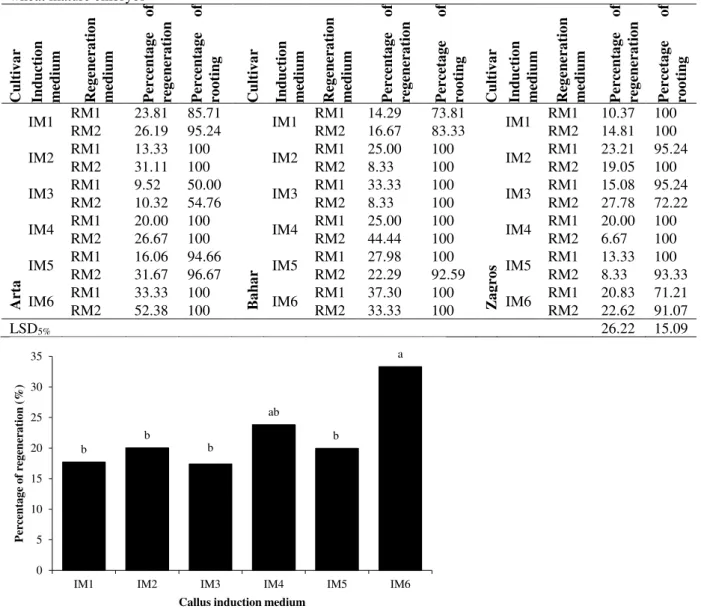
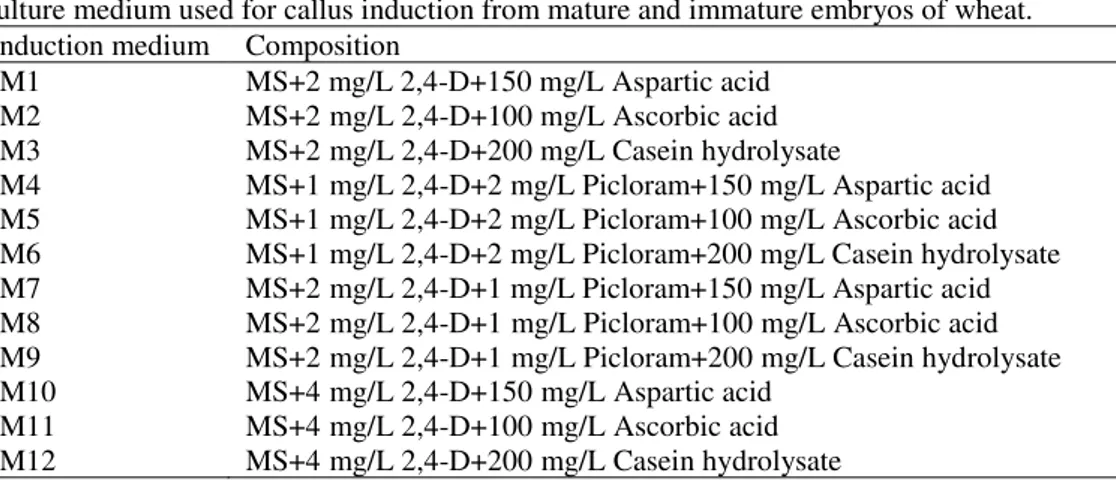
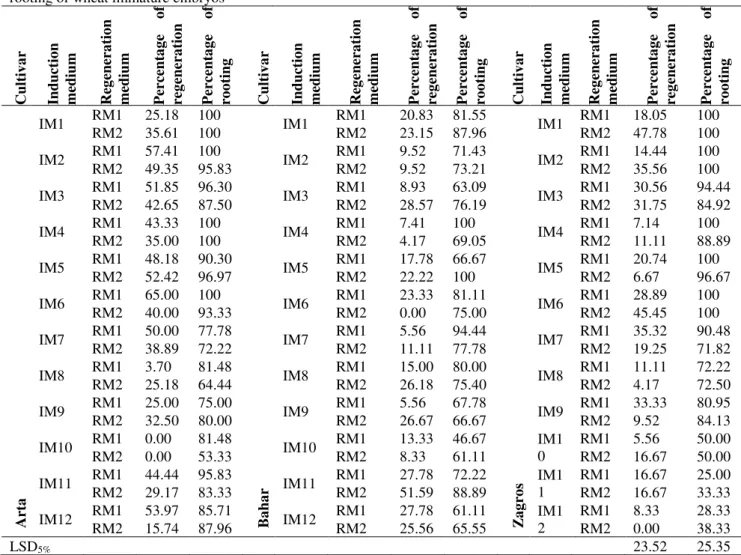
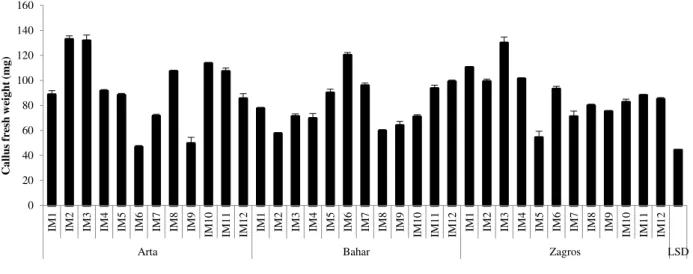
The addition of the auxins 2,4-D and Picloram, in the induction media of somatic embryogenesis favored the development of nodular embryogenic callus with differentiated
However, the plant regeneration frequency was lowest when somatic embryos induced on MS medium containing picloram or combination of 2,4-D and picloram were cultured on MS
Immature embryo tissues produced yellowish to white, nodular embryogenic callus, characterized by the formation of leaf-like structures, green shoots and rooted shoots