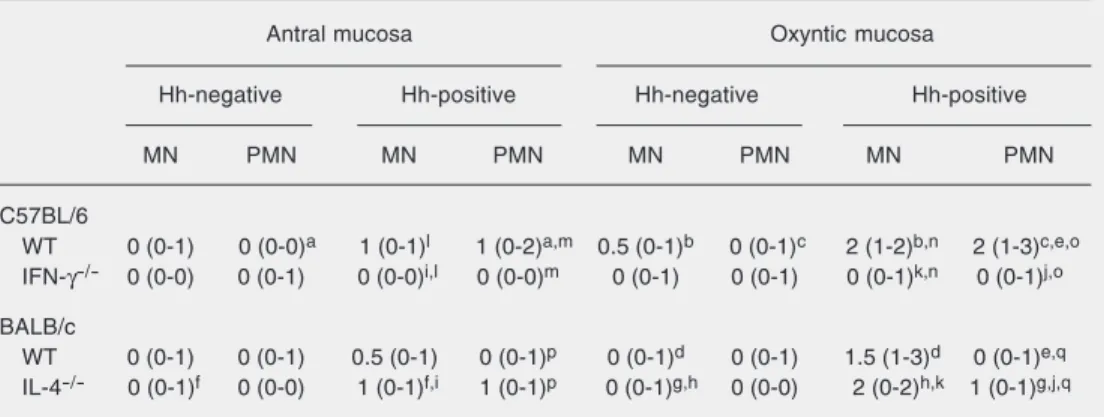
The role of IFN- γγγγγ and IL-4 in gastric mucosa inflammation associated with
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Ap´ os estabelecer os trˆ es tipos poss´ıveis de distribui¸c˜ oes limites extremais, o se- gundo problema de interesse da Teoria dos Valores Extremos consiste em determinar
Table 1: Means (x), standard deviation (sd) of IL-10 serum levels (pg/ml) in BALB/c mice treated with glucan (G5) and saline (G6), measured in five different moments before
Background: The present study evaluated the effect of treatment with benznidazole on mRNA expression of IFN- γ , IL- 17, IL-10, TGF- β and FoxP3 in spleen and heart tissue of
Therefore, in this work a comparative study among BALB/c, C57BL/6 and the IL-4-/- BALB mouse strains examined the evolution of the size of lesions, the archi- tectural tissue
In BALB/c mice, IL-4 production during the initial phase of infection with Leishmania major is necessary and sufficient to instruct TH2 cell development resulting in
Therefore, in this work a comparative study among BALB/c, C57BL/6 and the IL-4-/- BALB mouse strains examined the evolution of the size of lesions, the archi- tectural tissue
Thus, in the present study, we utilize a mouse model of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy and IL-4 knockout mice to investigate the possible role of IL-4 signaling
In these patients, lower concentrations of IL-4 and IL-10 in gastric biopsies were demon- strated when compared to patients with mild inflammation and neutrophil activity and