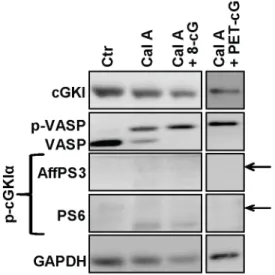
Catalytic activity of cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I in intact cells is independent of N-terminal autophosphorylation.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Sur cette base commune, des orientations distinctes se sont cependant développées ; – l’une, particulièrement représentée en Suisse romande, centrée sur un
This protein contains a serine protease domain in the N-terminal region that requires the formation of a non-co- valent complex with the membrane-bound cofactor NS2B for activity,
In its native background, the NifA activity is regulated by the prevailing ammonium levels and the N-terminal GAF domain of NifA has been implicated in
The sequence analyses of these proteins show that the Pso2p catalytic core is localized within the N-terminal part of the protein, while a DNA ligase I domain can be detected in the
is to present the development and comparison of n + pn + and n + pp + solar cells processed in p-type multicrystalline silicon wafers with screen printed metallization.. The n + pn
Considering that the N-terminal region of albumin is modiied when exposed to ischemia, hypoxia, acidosis and free radical damage, and that its presence in the serum
These results indicate that the two tyrosines in the amino-terminal part of the GIT1 polypeptide are needed for the interaction with the carboxy-terminal portion of the protein to
In this work, we report the expression of the N-terminal domain of TPL in Pichia pastoris to study the effect of the C-terminal domain deletion on the enzyme activity, and to verify