Braz. J. Phys. vol.35 número2A
Texto
Imagem
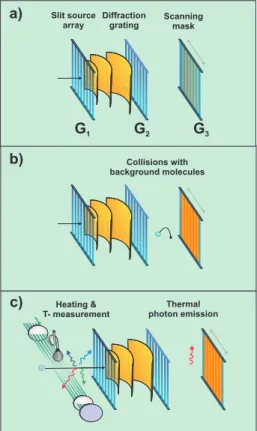
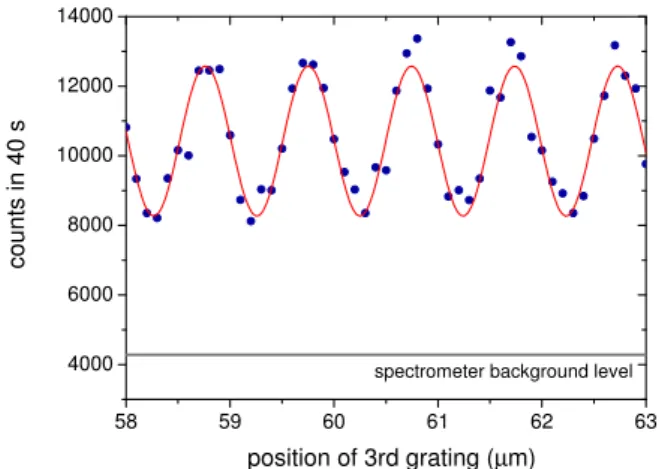
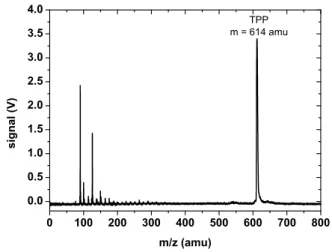
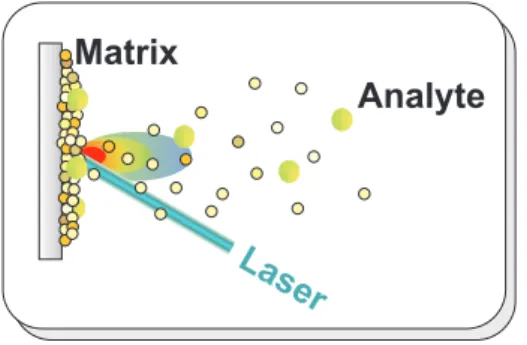
Documentos relacionados
Por sua vez, definem-se os seguintes objectivos específicos: (1) compreender as bases racionais que motivaram o interesse crescente da comunidade científica em torno
We show how the quantum to classical transition of the cosmological fluctuations produced during inflation can be described by means of the influence functional and the
These proceedings are based on the Invited Lectures and Contributed Papers of the Second International Work- shop on Decoherence, Information, Complexity and Entropy – DICE 2004,
Quantum computing has raised a problem opposite to the older ones encountered in measurement theory, namely how to avoid or delay the action of decoherence.. Whether or not this aim
The problem with the Schr¨odinger equation in relativistic quantum theory is in essence a matter of labels that one has to put on vectors in the Hilbert space to identify the states
It is clear that seemingly paradoxical behavior of quantum fidelity with respect to the classical correspondent is a consequence of the breakdown of quantum classical corre-
How- ever, it has been shown that this apparently paradoxical situ- ation can be resolved with the introduction of different time scales inside which the typical features of
We have demonstrated that in problems involving noise- induced escape of a classical field over a barrier, a type of second-order phase transition, with what appears to be at-
