The kinetics of zinc silicate leaching in sodium hydroxide
Texto
Imagem


![Fig. 8 shows the Log K app versus Log [NaOH] plot from which the reaction order with respect to the NaOH concentration was determined as 1.44±0.46](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/15696597.628224/6.892.76.401.87.251/shows-versus-naoh-reaction-order-respect-concentration-determined.webp)
Documentos relacionados
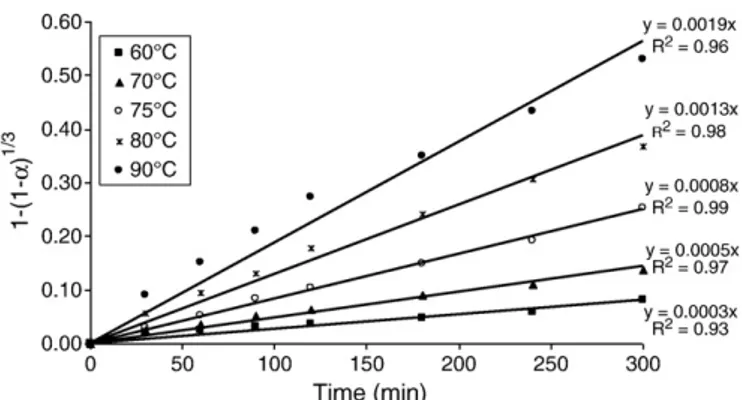
The Shrinking Core Model (SCM) with chemical reaction control and product layer diffusion control as well as the initial rate (IR) method were used to describe the dissolution
Firstly, the effects of temperature, ferric ion and sulphuric acid concentrations, agitation speed and particle size on the leaching kinetics of a zinc sulphide
Materials and Methods: The antilithiatic activity of sodium hydrogen sulfide (NaSH), sodium thiosulfate (Na 2 S 2 O 3 ) and sodium sulfate (Na 2 SO 4 ) on the kinetics of calcium
In order to examine the effects and the interaction of angiotensin II (ANG II, 1 pM) and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP, 1 µM) on the kinetics of bicarbonate reabsorption in the
iron and zinc in roasted molybdenum ore: effect of acid concentration, temperature, pulp density and leaching time were studied systematically.. The temperature study was carried
hydrazinolysis reaction for producing fatty N -acyl hydrazines 3a - c was tested in the presence of two strong bases, sodium hydroxide and sodium methoxide, which
Experiments to investigate the effects of the initial B[a]P concentration, contact time, and temperature on the adsorption kinetics and isotherms were conducted individually
The influence of the solvent concentration was evaluated using solutions of 10 mg L -1 folic acid in diferent concentrations of sodium hydroxide: 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mol L -1..