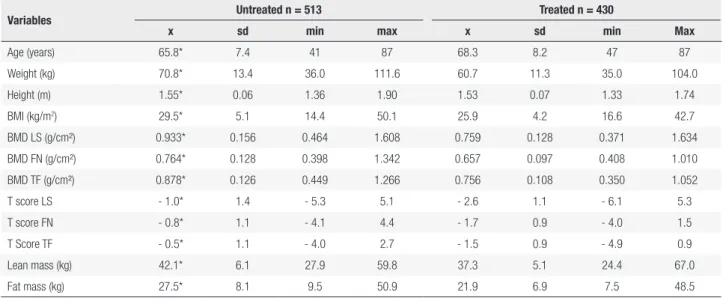
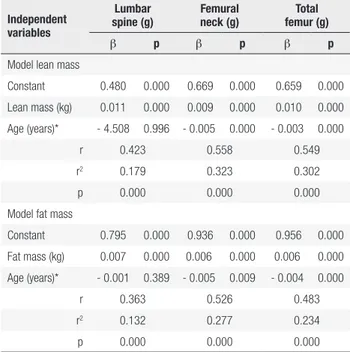
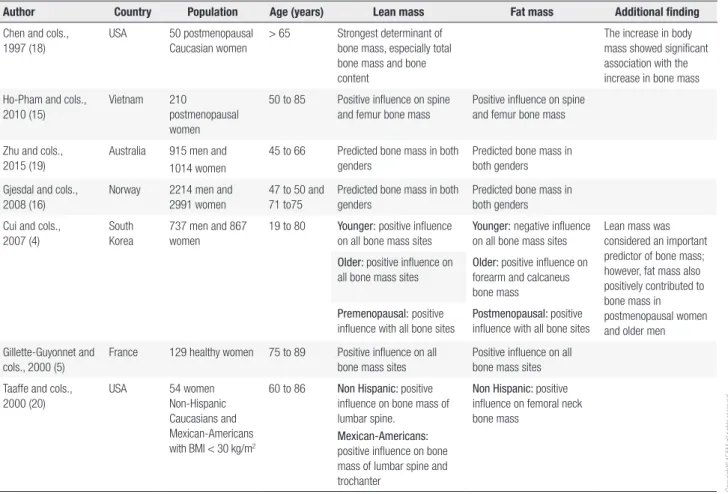
Lean mass as a determinant of bone mineral density of proximal femur in postmenopausal women
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Alguns pressupostos estabelecidos 9 de grande importância para guiar a prática assistencial, entre eles têm: As enfermeiras se aproximam da enfermagem como uma
middle-aged women with HIV infection have re- duced bone mineral density independent of the use of HAART and that the presence of osteopenia and osteoporosis cannot be
Aim - To study a possible relationship between chronic gastritis, parietal cell density of the oxyntic mucosa and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, as chronic
Effects of zoledronate versus placebo on spine bone mineral density and microarchitecture assessed by the trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a
concluded that The prevalence of abnormal bone mineral density (BMD) was higher in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors (BCS) than in postmenopausal women without breast cancer”..
Spearman correlation between intake variables and BMD of 25 women diagnosed with osteopenia or osteoporosis in the post-menopausal period, participants of the Practice of
Histomorphometry of the distal femur showed a decrease in trabecular volume in the untreated group (OVX), and an increase in the two treated groups, principally in the
Associations of vitamin D status with bone mineral density, bone turnover, bone loss and fracture risk in healthy postmenopausal women. The OFELY