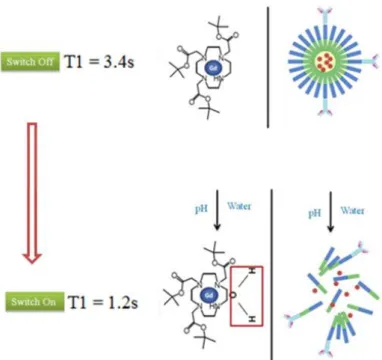
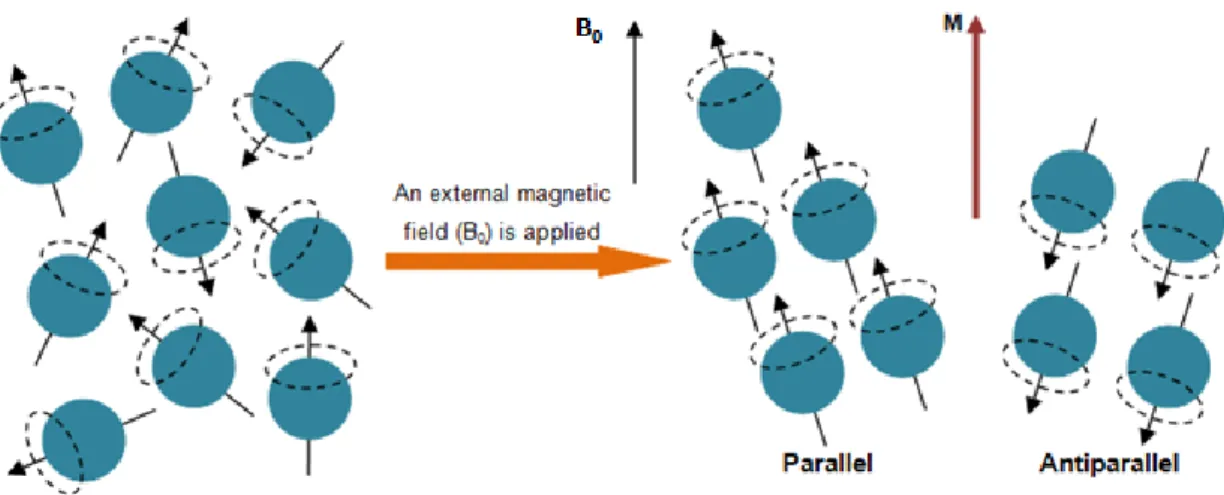
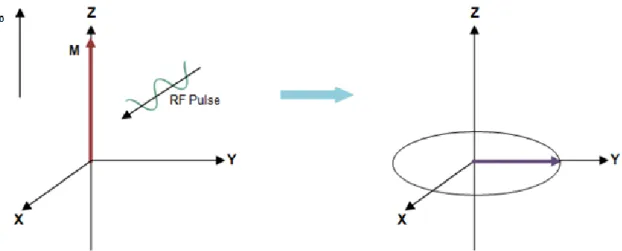
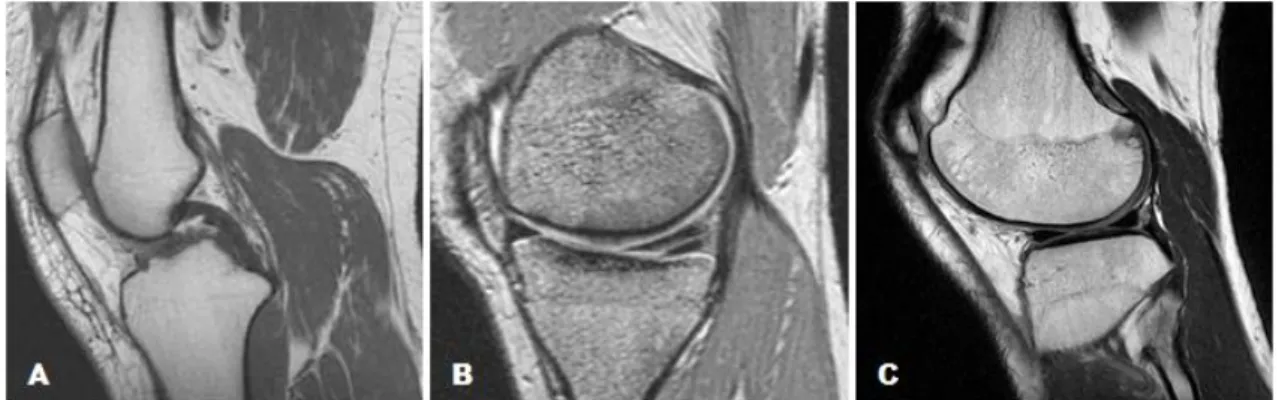
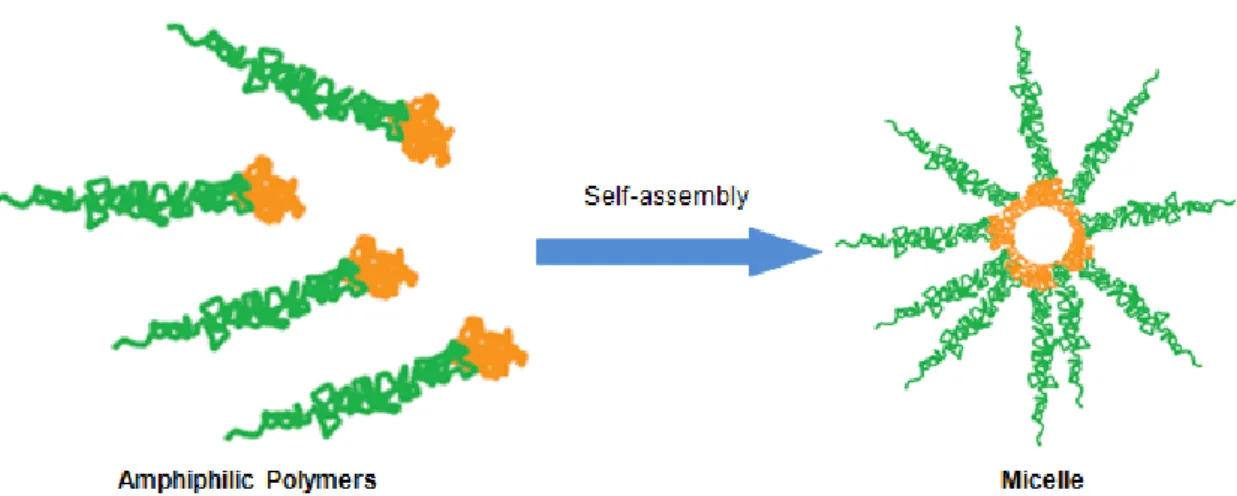
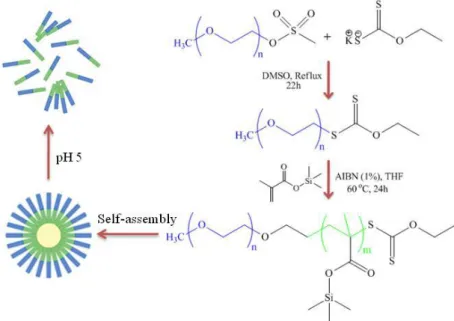
Self-assembled nanoparticles as new smart contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry in the lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: a series of 100 patients. Connelly A,
Our study aimed at introducing and describing the infarction size quantification on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging using the delayed contrast- enhanced technique, and at
Magnetic resonance imaging: dynamic contrast enhancement and diffusion-weighted imaging to identify malignant cervical lymph nodes..
The authors presented their pioneering work emphasizing that after appropriate validation this new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and MRI / magnetic resonance spectroscopic
Objectives: To evaluate the use of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with β -thalassemia and to compare T2* magnetic resonance imaging results with
Objective: To assess intracellular labeling and quantification by magnetic resonance imaging using iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles coated with biocompatible materials in rat
Source: Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies, and biomedical applications (13), and In situ doxorubicin
Characterization by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of neurovascular compression and structural alterations of trigeminal nerves in patients with primary