Effect of alendronate on bonespecific alkaline phosphatase on periodontal bone loss in rats
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
§ 7 o Os contribuintes que optarem pelo pagamento ou parcelamento dos débitos nos termos deste artigo poderão liquidar os valores correspondentes a multa, de mora ou de
Acemannan sponges stimulate alveolar bone, ce - mentum and periodontal ligament regeneration in a class II furcation defect model. Influence of interleukin-1 gene polymorphism
The results of the present study suggest that if alcohol consumption exacerbates alveolar bone loss, the observed effect of drinking on increasing periodontal
The aim of this study was to evaluate, by histological analysis, the effect of growth hormone (GH) on periodontal ligament and alveolar bone during experimental tooth movement
maritima 5mg/kg had a protective effect on experimental periodontitis due to the inhibition of inflammatory parameters, alveolar bone loss and oxidative stress markers, representing
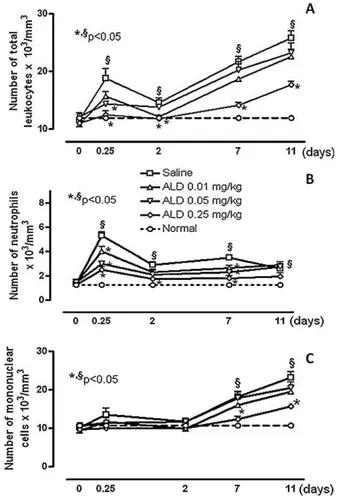
In summary, rats subjected to periodontitis and treated with the lower-dose combination of ALD and ATV, administered prophylactically or therapeutically, showed a reduction
Photomicrographs from the buccal gingiva of rats subjected to periodontitis. The buccal gingivae from the region of the left upper molars were removed. A) Normal gingiva; B)
Histopathological analysis indicated intense alveolar bone and cementum resorption, associated to important infiltration of inflammatory cells (p<0.05) on SAL group (Table