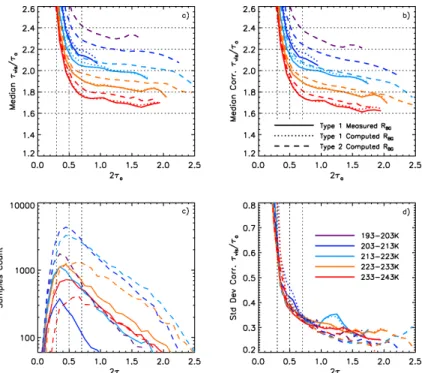
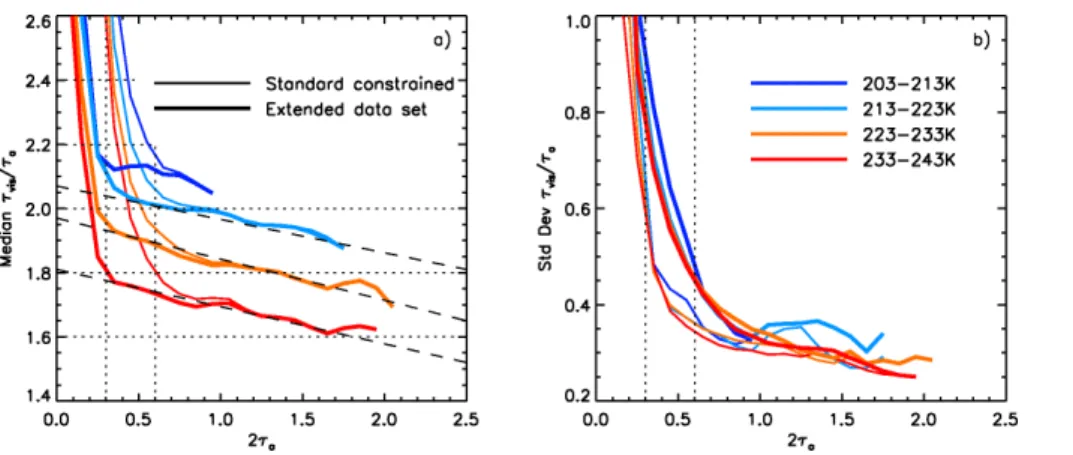
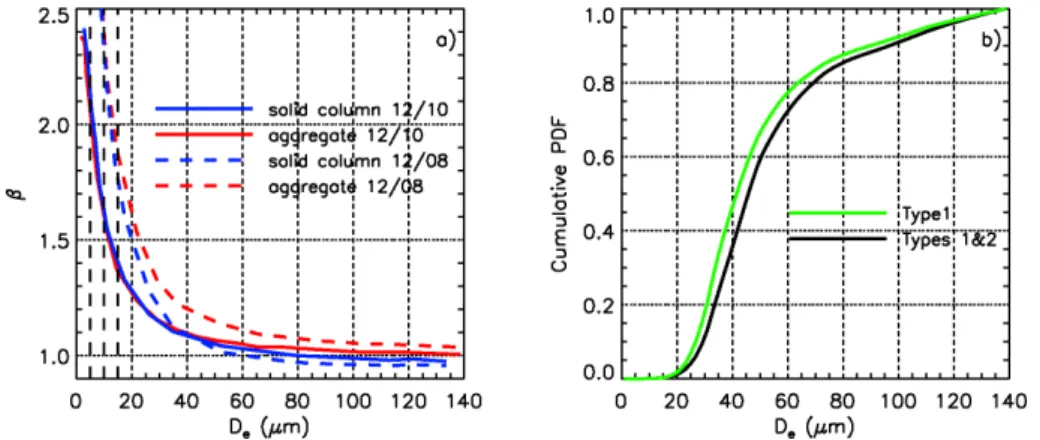
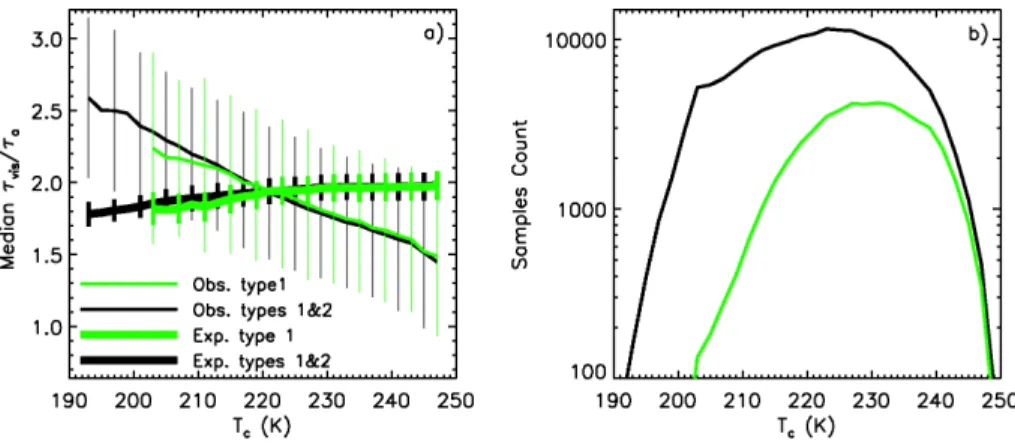
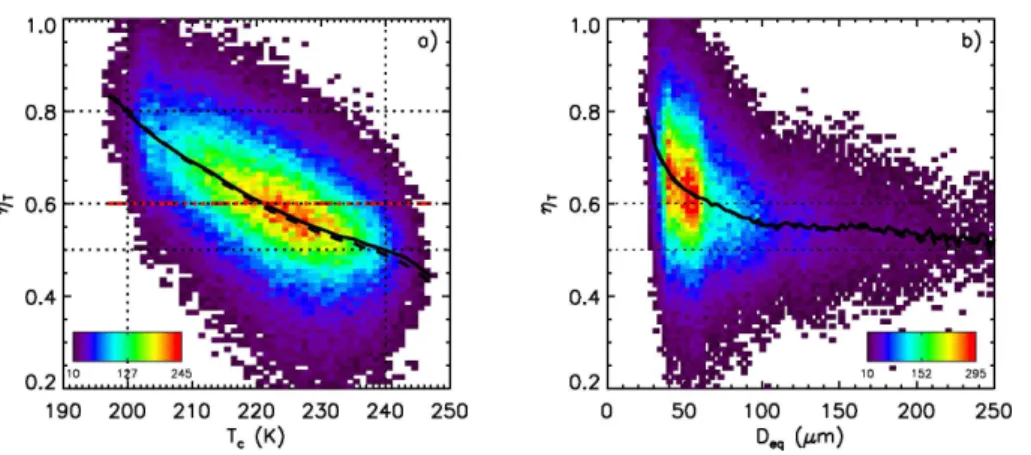
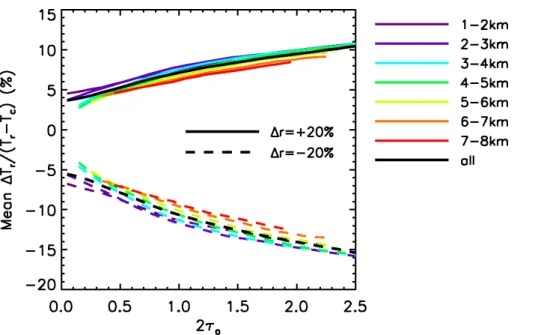
Optical depths of semi-transparent cirrus clouds over oceans from CALIPSO infrared radiometer and lidar measurements, and an evaluation of the lidar multiple scattering factor
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Apparent scattering ratios calculated from the two lidar measurements of to- tal attenuated backscatter at 532 nm show similar aerosol and cloud layer structures both under
Data for direct evaluation of the obtained mean vertical profiles were taken from the dataset of Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) onboard the NASA
Figure 3 shows cloud-top heights, optical thickness, asym- metry parameter, distortion and aspect ratio retrieved from RSP measurements as a function of time, along with CRS
The cloud optical thickness and the droplet e ff ective radius are retrieved from spectral radiance data in nadir and and from hyperspectral radiances in a 40 ◦ field of view..
Cloud-top temperatures are significantly negatively correlated with increasing aerosol index (AI) over oceans and aerosol optical depth (AOT) over land for deep mixed-phase clouds
measured from Terra are also compared to LBLMS simulations in cloudy conditions using retrieved cloud optical depth and e ff ective radius from MODIS. Three case stud- ies are
We analyzed the mean optical properties of southern hemisphere midlatitude tropopause cirrus, such as optical depth, extinction coefficient and lidar ratio using lidar observations
Temperature measurements from the ALOMAR Weber Na lidar together with cosmic radio noise absorption measurements from IRIS and particle measurements from NOAA 15, 16 and 17 are used