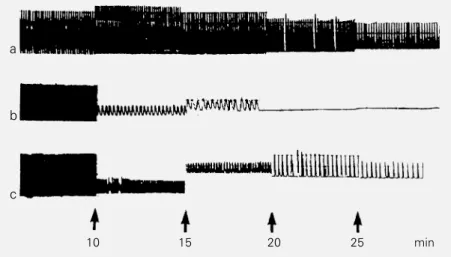
Effect of trolox C on cardiac contracture induced by hydrogen peroxide
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
The authors proposed that since ED was proven to be an early sign of coronary heart disease, it is reasonable to believe that extra-oral inlammation induced by periodontal
It might be possible that noradrenergic pathway and alpha-2 and beta-receptors participate of the analgesia modulation induced by TENS, since the administra- tion of yohimbine
The pathophysiology of cardiac syndrome X is still being debated; however, endothelial dysfunction leading to a reduced coronary microvascular dilatory response and increased
This study demonstrated that in elderly patients with stable coronary atherosclerosis, exercise-induced myocardial ischemia and minimal ventricular dysfunction, the heart rate at
Role of nitric oxide of the median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) in the alterations of salivary flow, arterial pressure and heart rate induced by injection of pilocarpine into the MnPO
It should be pointed out that the high percentage of abnormal seedlings and dead seeds in the germination and cold tests (Table 2), resulting from seeds that did not present
Este trabalho teve dois objetivos claros: o primeiro foi sintetizar nanopartículas de sulfuretos metálicos e respetivos nanocompósitos de dióxido de titânio (TiO 2 ), com recurso
Effect of rosiglitazone on progression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes melli- tus and coronary artery disease: the assessment on the