A DNA enzyme targeting Egr-1 inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by down-regulation of cyclin D1 and TGF-β1
Texto
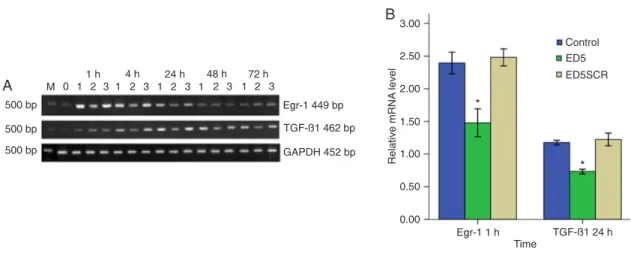
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
The difference in the methylation pattern of STEAP1 between PNT1A and LNCaP cells, along with the increased STEAP1 mRNA expression in response to DNMT and HDAC
Increased bioavailability of ROS influences cellular processes leading to vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) growth, inflammation, migration and extracellular matrix (ECM)
The siRNA knockdown of RBP2 expression in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) reduced levels of a -smooth muscle actin ( a -SMA) and vimentin and decreased the proliferation of HSCs;
TGF-b1 is a multifunctional cytokine, a potent inhibi- tor of epithelial cell repair and an inducer of a hyper- trophic and hypercontractile arterial smooth muscle cells
Furthermore, it was shown that feeding GABA may significantly improve the immune responses of heat-stressed chickens by increasing the expression levels of IL-1 and TGF-β1,
was the relationship between megakaryocyte TGF  1 expression, MVD and bone marrow fibrosis, suggesting a possible mechanism by which increased levels of TGF  1 produced
An- other study found an increase in TGF-β1 serum levels only in patients with the stage A of the cardiac form (Clark et al. 2015), while TGF-β1 serum levels did not
OMT treatment significantly decreased serum TGF-β1 levels, fibrous deposition in rat liver tissues, the thickness of the fibrous septa, inflammatory cell