Infection with human papillomaviruses of sexual partners of women having cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Texto
Imagem
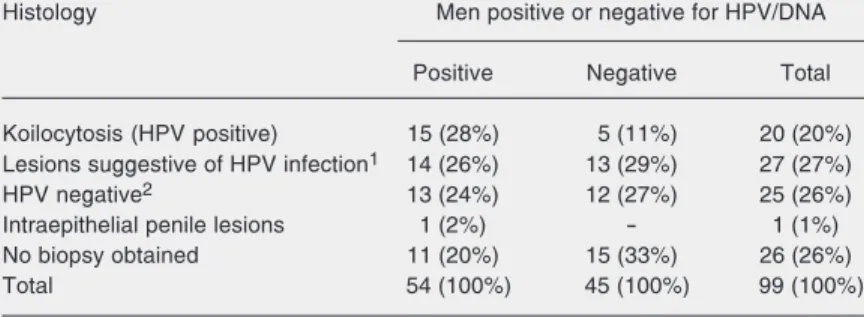

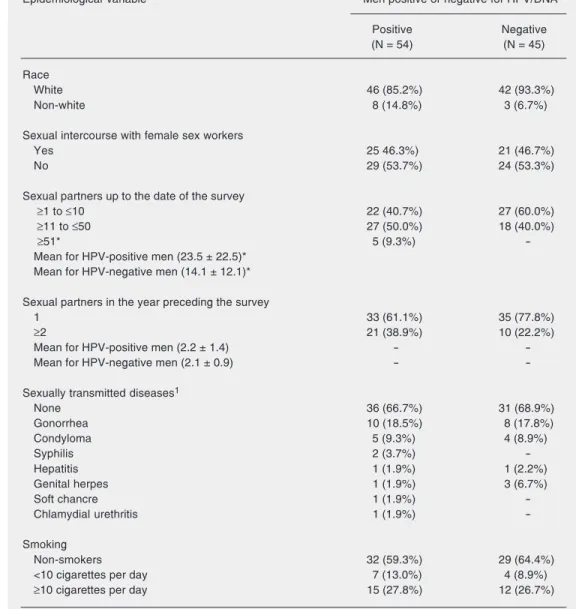
Documentos relacionados
Early initiation of sexual relations was associated with increased risk of invasive cervical cancer regardless of the number of sex partners and other
Neither male nor female nor any other gender identification implies the choice of sex object, genders of partners or sexual practices.. Key words : Sexual identity, choice of
We investigated sociodemographic variables (sex, schooling, age, marital status, and income); work-re- lated variables (occupation, manipulation of blood); sexual behavior
The independent variables tested were: sociodemographic (sex, age group, marital status, race/color, level of schooling, paid work), life habits (physical and sexual
Unprotected sexual activity was more frequent with irst sexual intercourse before the age of 13, commercial sexual exploitation, multiple sexual partners, intrafamily violence
of the participants reported not having used a condom during the last vaginal sexual intercourse,.. 48.4% did not use a condom during the last oral sex, while 26.3% reported not
This variable was not statistically signifi cant when associated with use of the male condom by partners or cli- ents, although most of the women with up to eight years of
Anal/vaginal receptive sex is riskier than insertive prac- tices. Sex acts with partners of unknown/positive HIV status are riskier than those with HIV-negative partners, regardless