Rev. Saúde Pública vol.41 número4
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The comparison of the mean systolic and diastolic factors associated with stenosis of the renal graft artery blood pressure and creatinine levels, as well as the number of
Objective: To analyze the prevalence of dipping in hypertensive individuals, to correlate dipping to the blood pressure levels, clinic, and socio-demographic factors, and
Objective: To evaluate the response of systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressure, heart rate (HR) and rate-pressure product (RPP) to pre- and postprandial exercise.. Methods: Ten
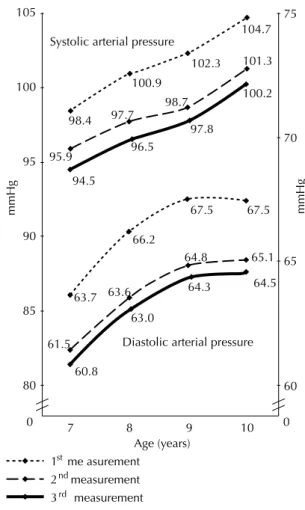
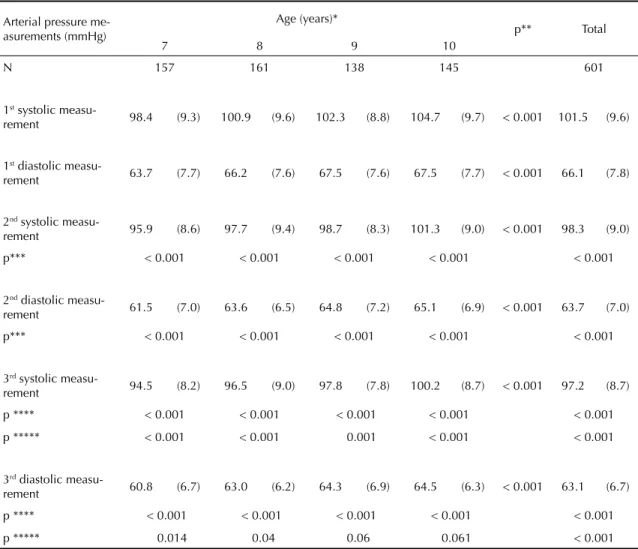
In our study, the higher levels of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the univariate analysis were significantly associated with white children, children from the region with
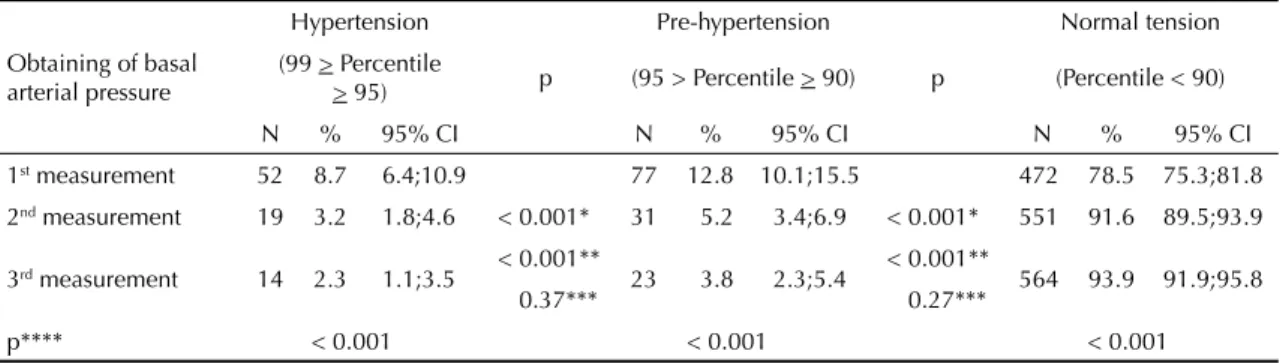
Conclusion - Our study showed that the prevalence of systemic hypertension was 31.5%, and that 27.6% of the individuals interviewed had blood pressure levels under control at the
Objective: To evaluate the relationship among the casual blood pressure with hyper-reactive response on ET and to compare Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) data
The objective of this study was to show how positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), applied at different levels, interferes with systolic arterial pressure (SAP), diastolic arterial
Objective: To compare the acute cardiovascular responses of systolic arterial pressure (SAP), diastolic arterial pressure (DAP), heart rate (HR) and double product (DP) during