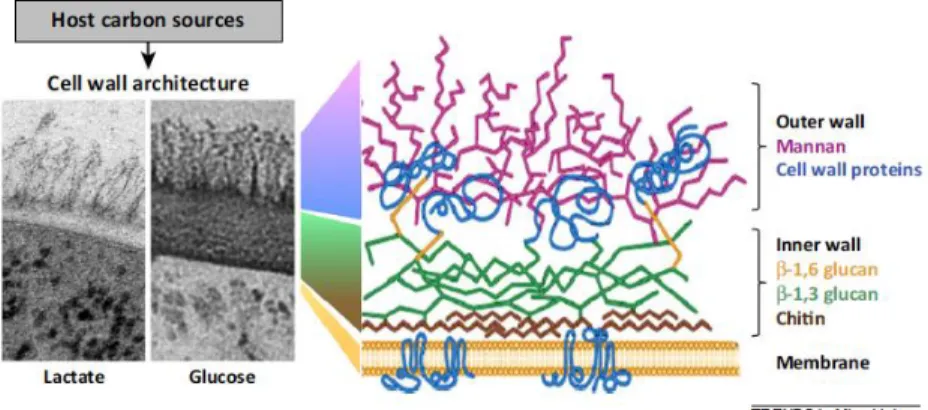
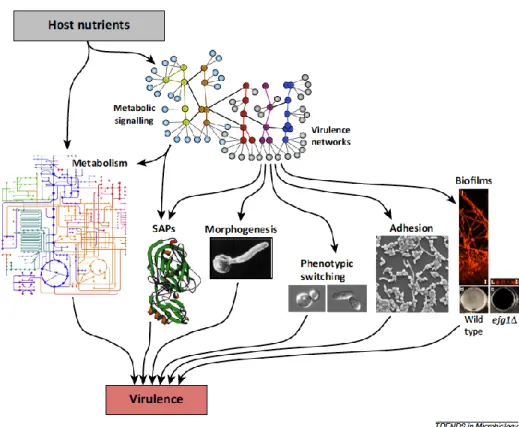
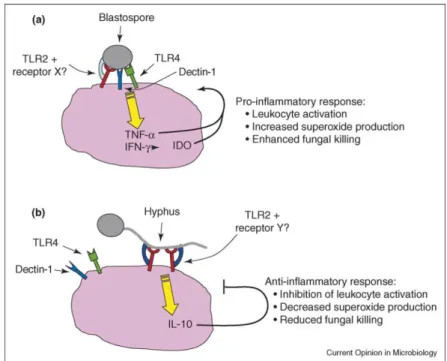
The impact of carbon source in Candida albicans virulence: participation of RLM1 in pathogen host interaction
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Após perceber os constantes desafios surgidos da vivência cotidiana da comunidade, o processo acelerado de mudanças urbanas que atinge as favelas da Zona Sul e
Assim sendo, a região do Alentejo caracteriza-se por ser uma região receptora, ao contrário da região de Lisboa e Vale do Tejo que se apresenta como contribuidora líquida uma vez que
As shown in Table 1 and Figure 1, anticancer drugs effectively prevent yeast to hyphal form transition induced by 10% se- rum.. Among the four antimicrotubule anticancer
Características Ambiente 15 Animais 3 Astrologia 8 Celebridades 146 Cidades 43 Cinema e TV 51 Cultura 3 Economia 91 Educação 2 Desporto 185 Life Style 21 Internacional 37 Política
A empresa está presente em mais de 600 países, o que a torna atraente como opção para facilitar o transporte não apenas de residentes, mas especialmente de turistas que desconheçam
8.5- ANEXO E – Ficha técnica do indicador tático: Taxa de Cobertura Assistencial Total Por Classificação de Prioridade Fisioterapêutica C1, C2, C3, C4, C5... 8.6- ANEXO F –
Although Candida albicans is the most frequently-isolated species related to oral opportunistic infections, an increase in the frequency of oral infections caused by non- albicans
Figure 20 Original image (left), guided Grad-CAM (center) and precision-recall (PR) plot (right) for pneumothorax class. The Grad-CAM shows that the CNN is getting a hot region on