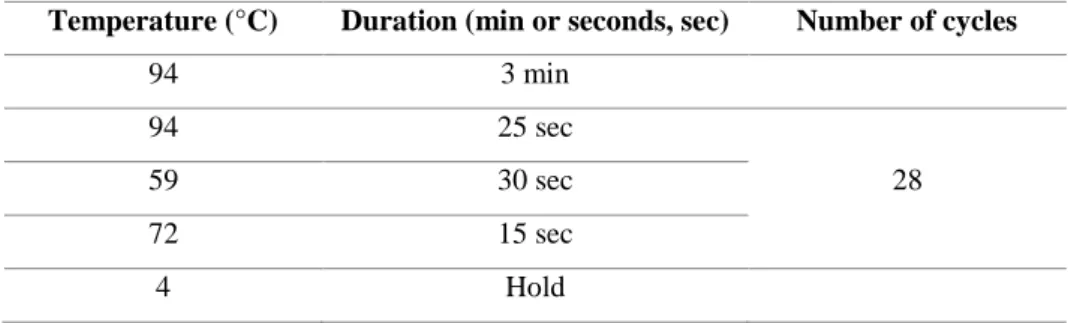
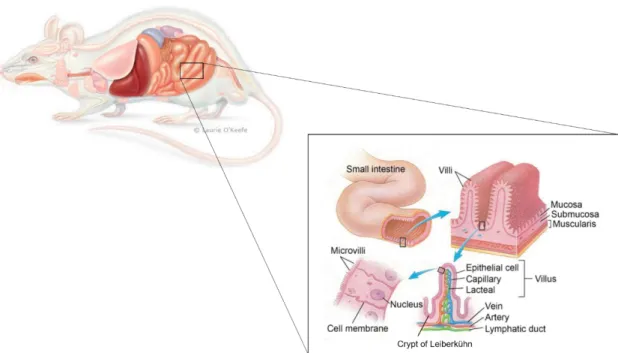
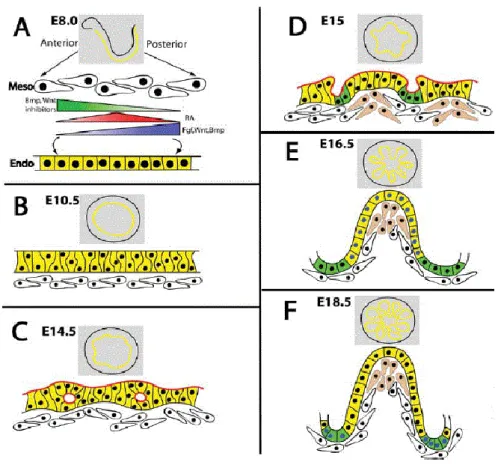
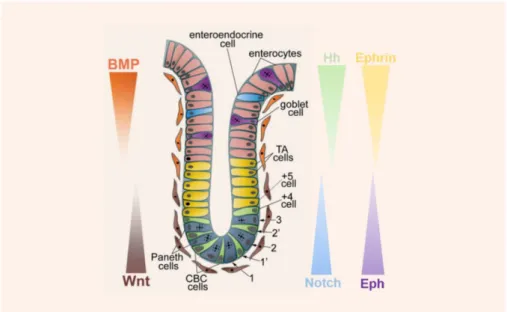
Establishing a Diphtheria Toxin-sensitive system for cell ablation within the embryonic small intestine in mouse
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
that embryonic stem cells in a specific culture medium may originate lung progenitor cells and have several ad- vantages: (1) better cell integration with the host tissue, (2)
Endogenous stages of Cyclospora schneideri n.sp., in the epithelial cells of the small intestine of the snake Anilius scytale scytale , as seen in histological sections.. Figs 1,
This paper reports the clinical and radiological aspects of the small intestine within two months after infection in patients with the toxemic acute form of
Increased proliferation of human synovial mesen- chymal stem cells with autologous human serum: compari- sons with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and with fetal bovine serum.
Human intestinal epithelial cells (HIEC, lane 1 ), human intestinal mesenchymal cells (HIM, lane 2 ), 18-week fetal small intestine ( lane 3 ), and Caco-2 cells ( lane 4 )
We examined in vitro the characteristics of embryonic cells of Rhipicephalus microplus and Amblyomma cajennense in cell culture and investigated the suitability of embryonic
Our findings support the effects of glutamine on villus and crypt development in the small intestine: increased villus height and reduced crypt depth, suggesting that glutamine
Here, we describe the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSc) from head-derived primary culture of mouse embryonic cells using small chemical inhibitors of the MEK