Study of Mechanical and Wear Behaviour of Hyper-Eutectic Al-Si Automotive Alloy Through Fe, Ni and Cr Addition
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Phase Formation, Thermal Stability and Mechanical Properties of a Cu-Al-Ni-Mn Shape Memory Alloy Prepared by Selective Laser Melting.. Piter Gargarella a * , Cláudio Shyinti
A melt-spun Fe 90 Si 5 B 5 alloy ribbon consists of bcc-Fe(Si) + Fe 3 B + amorphous phase and exhibits good bending ductility, high tensile fracture strength above 1000 MPa,
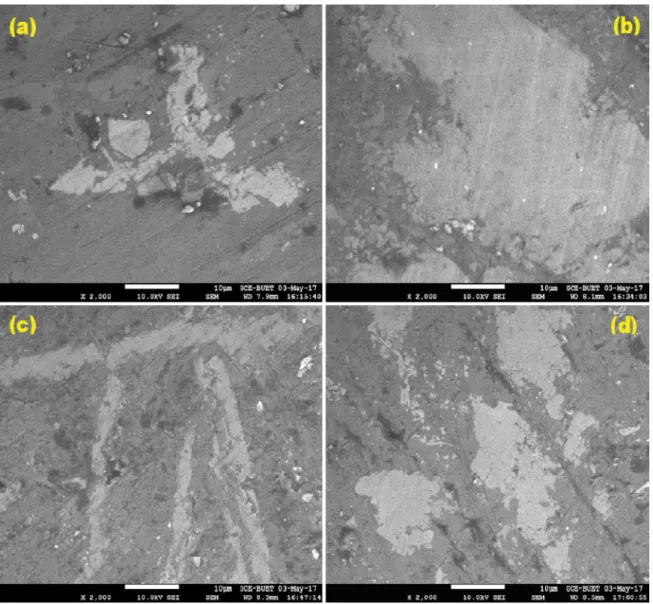
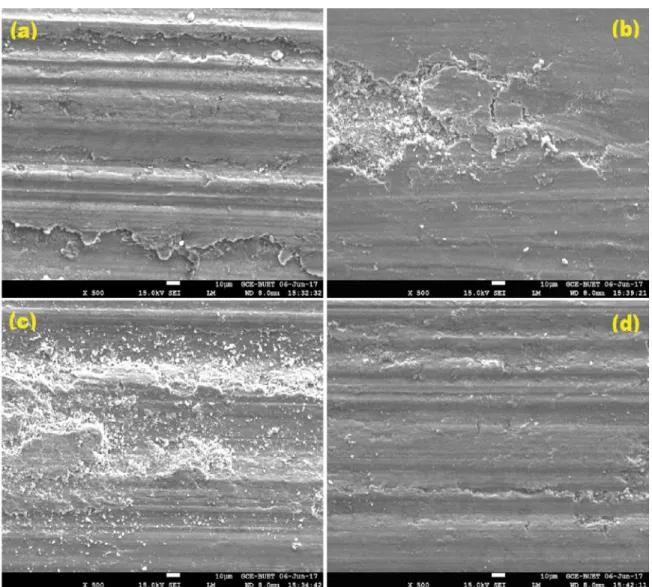
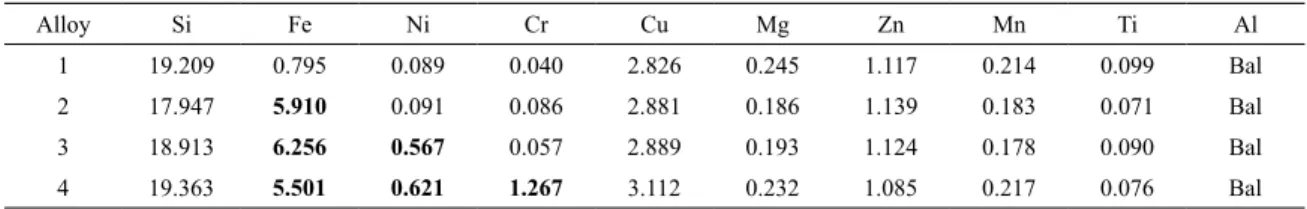
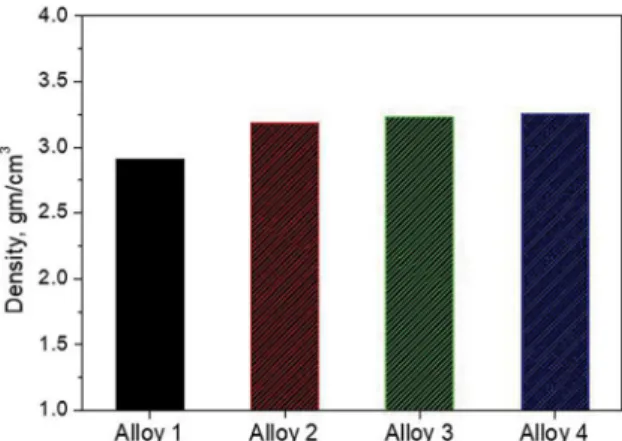
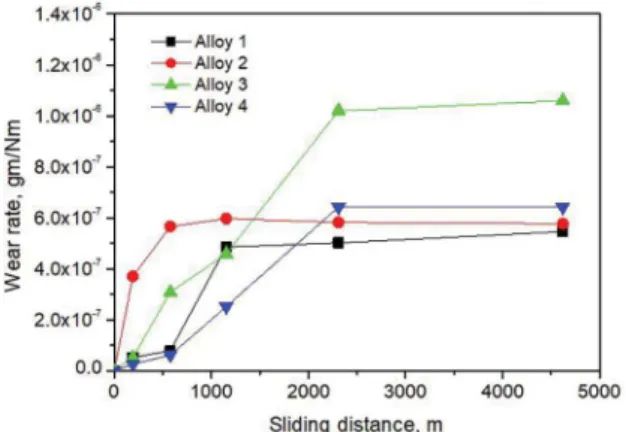
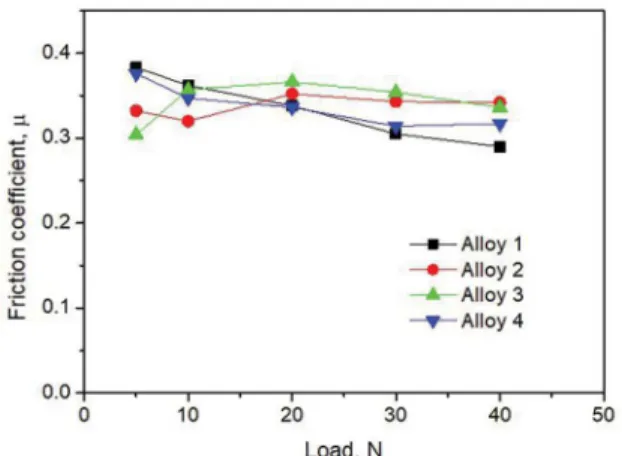
The purpose of the present work is to improve the mechanical properties (elongation % and strength) of the hypereutectic Al-Si alloy using rapid solidiication, addition
For the Al-Si5Cu3 alloy the results obtained in this work conirm that cooling rates inluence the nucleation and growth of α c -Al 15 (Fe,Mn) 3 Si 2 and β- Al 5 FeSi phases.
Relative molar amounts of Fe(II), Ni(II) and Fe(III) and the divalent/trivalent ratio in the Ni(II)-GR2 samples as a function of the divalent ion ratio Fe(II)/Ni(II) in the
This study evaluated the bonding characteristics of three commercially available porcelains fused to three Ni-Cr alloys and one experimental Co-Cr-Ti alloy, using a modified
The potenciodynamic curves of the dental alloys showed that the Ni-based dental alloy with >70 wt% of Ni had a similar curve and the Co-Cr dental alloy showed a low current
For the Al-Si5Cu3 alloy the results obtained in this work confirm that cooling rates influence the nucleation and growth of α c -Al 15 (Fe,Mn) 3 Si 2 and β- Al 5 FeSi phases.