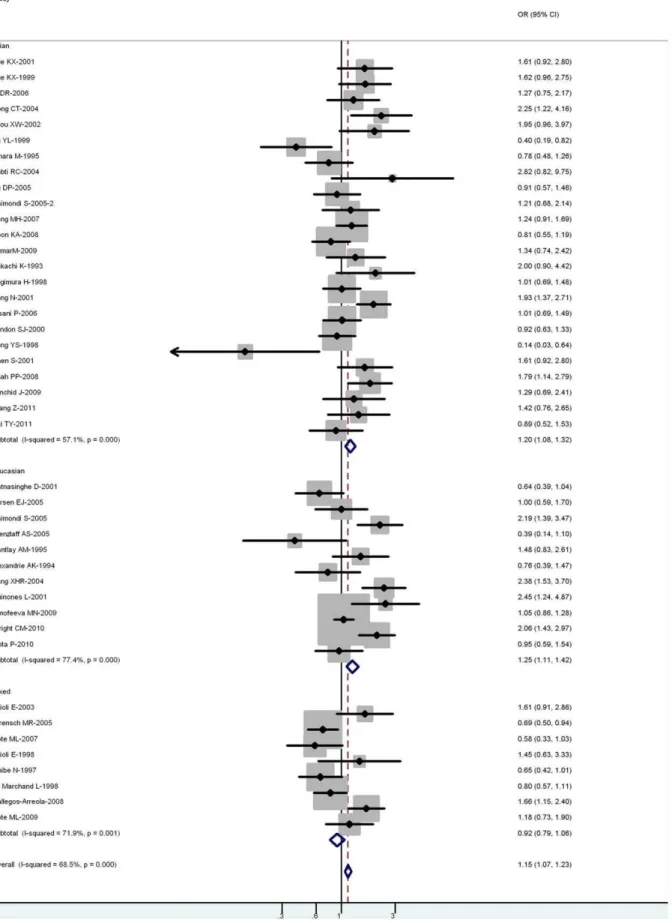
CYP1A1 Ile462Val polymorphism contributes to lung cancer susceptibility among lung squamous carcinoma and smokers: a meta-analysis.
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
To compare the ADCmean values and ADCmin values among histologic types of adenocar- cinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and small cell lung cancer, analysis of variance was used.. The
trial demonstrated that selenium supplementation may reduce risk of cancer including lung cancer among those with lower serum selenium ( , 106 ng/mL) [38], and a second study in
Association of folate-pathway gene polymorphisms with the risk of prostate cancer: a population-based nested case-control study, systematic review, and meta- analysis.. Cancer
In September 2011, at the European Multidisciplinary Cancer Congress, in Stockholm, the association between EGF+61A/G polymorphisms and the risk of non-small-cell lung
In this meta-analysis, no association of the IL-10 2 1082A/G polymorphism with IS risk was found under all comparisons, and in subgroup analysis by ethnicity or source of
The distribution of the Bax-β48GA polymorphism frequency among cases and controls of the seven studies in different cancer types (CLL, squamous cell carcinoma,
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (1) the study as- sessed the association between hepatocellular carcinoma risk and COX-2
Many studies have linked tumor development and progression to the amplification and overexpression of STK15 in multiple human cancers (such as breast cancer, colorectal
