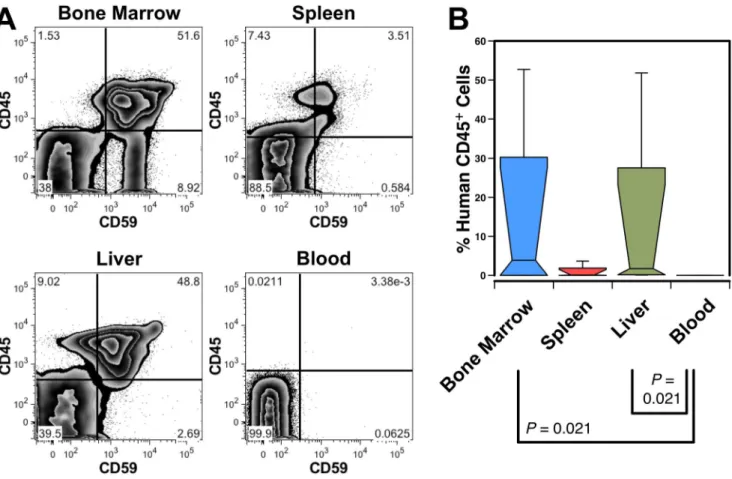
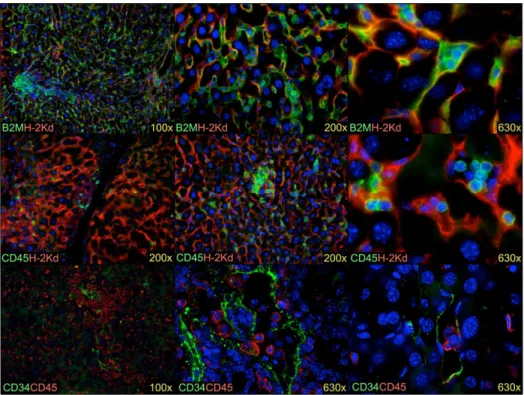
The adult livers of immunodeficient mice support human hematopoiesis: evidence for a hepatic mast cell population that develops early in human ontogeny.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Em suma, poder-se-ia dizer que o têrmo ciência é aplicável à administração pública sempre que alguns de seus métodos possam seguir princípios cinetíficos,
(β01β) In vivo hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood after transplantation into mice with liver injury. (β007)
Therefore, we examined EpCAM expression in a panel of human cancer cell lines and their respective primary tumour xenografts in immunodeficient SCID mice in order to identify a
There is other stem cell research that does not involve the destruction of a human embryo involving adult stem cells, amniotic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem
We used human CD8 + T cell clones to compare the ability of neonatal and adult monocyte-derived dendritic cells to present or process and present antigen using the MHC class I
We had previously found that embryonic yolk sac hematopoietic stem cells (YS-HSCs) are more sensitive to benzene toxicity than the adult bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells, and
Then, tumorigenic potential of adult human multipotent neural cells (ahMNCs) immortalized by the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene was examined as a stem cell