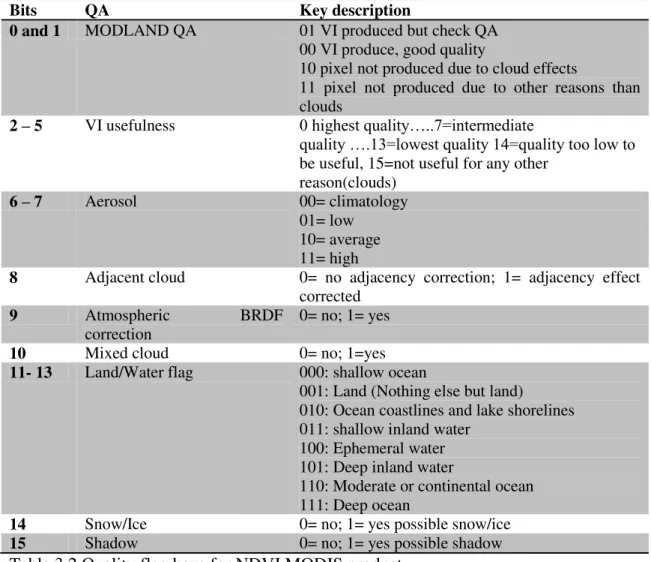
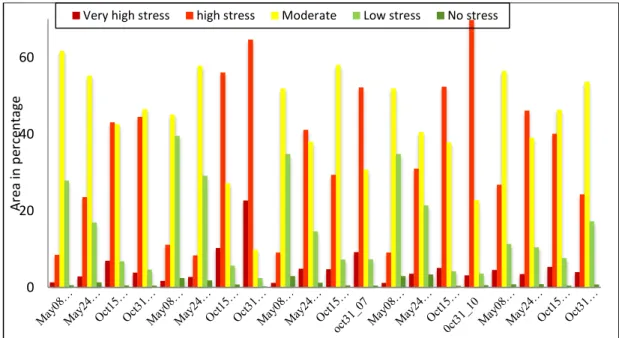
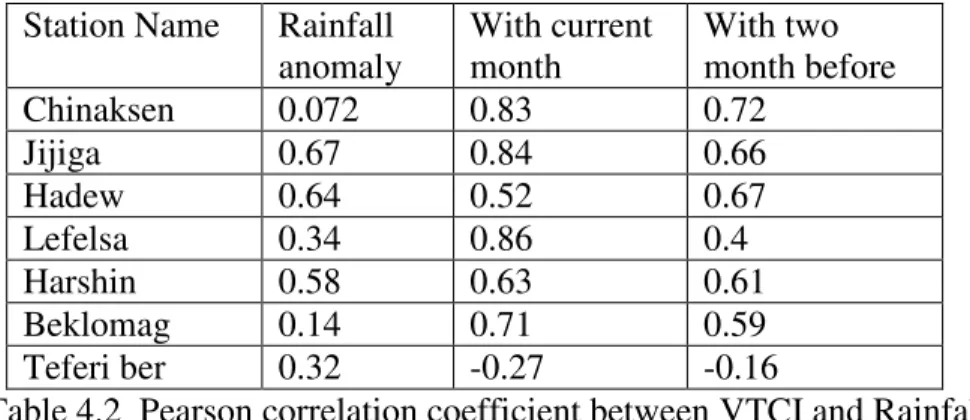
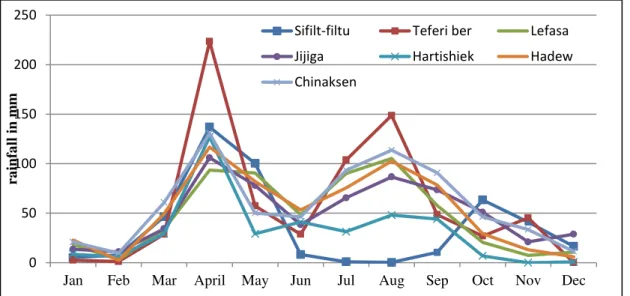
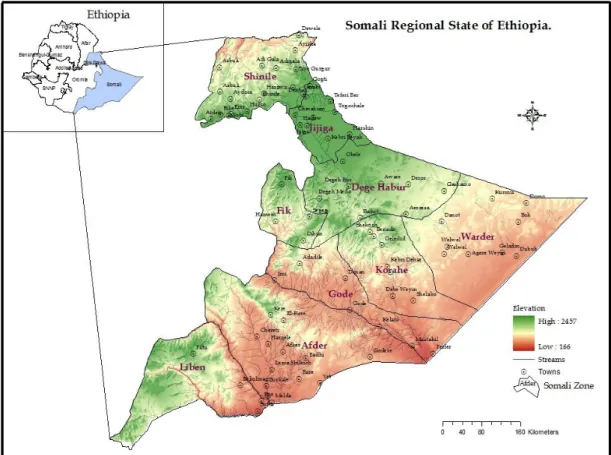
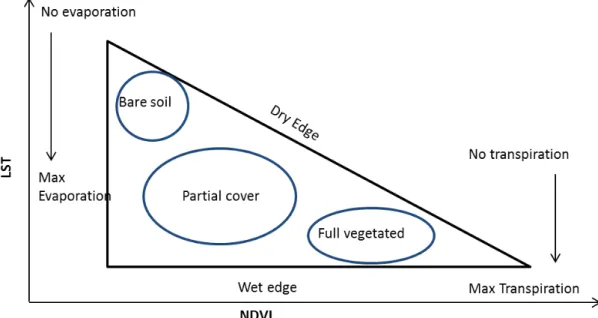
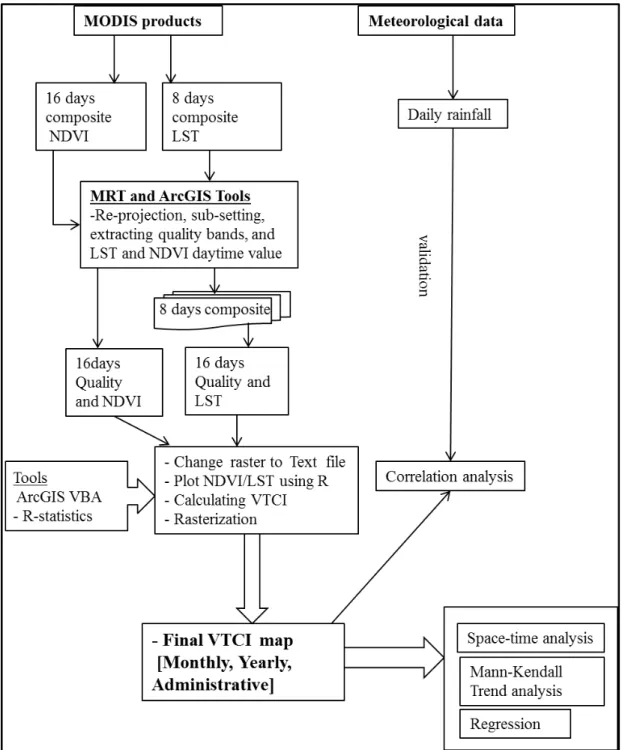
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF RECENT DROUGHT USING VEGETATION TEMPERATURE CONDITION INDEX
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
This study focuses on evaluation of the drought characteristics such as intensity, frequency and duration drought using Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in different time
We tested nestedness using NODF index and evaluated the environmental variability using the multivariate homogeneity of group dispersions (PERMDISP), separately for flood and
Surveying for drought tolerant accessions has resulted in the establishment of a drought tolerant core collection (Babic et al., 2011). Herein, the results of grain quality
Spectral indices used for drought monitoring: NDVI, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index; EVI2, Enhanced Vegetation Index; GVMI, Global Vegetation Moisture Index; NDI6 and
This could be confirmed by the analysis of the historical drought in the summer of 2003 compared to a scenario with drier ini- tial conditions as the storages for the
Typically, precipitation and temperature fore- casts, either from dynamic models or climatology resampling (i.e., ensemble streamflow prediction, ESP method; Mo et al., 2012), are
This study assessed the e ff ect of using observed monthly leaf area index (LAI) on hydrologic model performance and the simulation of streamflow during drought using the
– While the numerical values of the standardised drought severity index can be re- lated to very di ff erent local circumstances, a continent-wide tendency might be re- lated to