Mucosal acidification increases hydrogen sulfide release through up-regulating gene and protein expressions of cystathionine gamma-lyase in the rat gastric mucosa
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Other studies reported that glibenclamide pretreatment prevented the protective effects of NaHS and Lawesson’s reagent against ethanol (13) and NSAIDs (12) induced macroscopic
is important in the control of mucus production, blood flow, mucosal defense (using an ethanol-induced gastric damage model; a dependent effect, at least in part due to the reduction
Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and expression of c-myc, Bcl-2, and Bax protein in different gastric mucosa lesions. Effect of Helicobacter pylori
(D) and (I) show the gastric mucosa and the medial intestine, respectively, and preservation of the gastric mucosa in rats treated with naproxen and epiisopiloturine hydrochloride
Other studies reported that glibenclamide pretreatment prevented the protective effects of NaHS and Lawesson’s reagent against ethanol (13) and NSAIDs (12) induced macroscopic
In the present study we investigated whether changes in gastric mo- tility concerning the proximal stomach and gastric emptying of liquid meals correlated with mucosal lesions
Nitric oxide- induced synthesis of hydrogen sulfide alleviates osmotic stress in wheat seedlings through sustaining antioxidant enzymes, osmolyte accumulation and
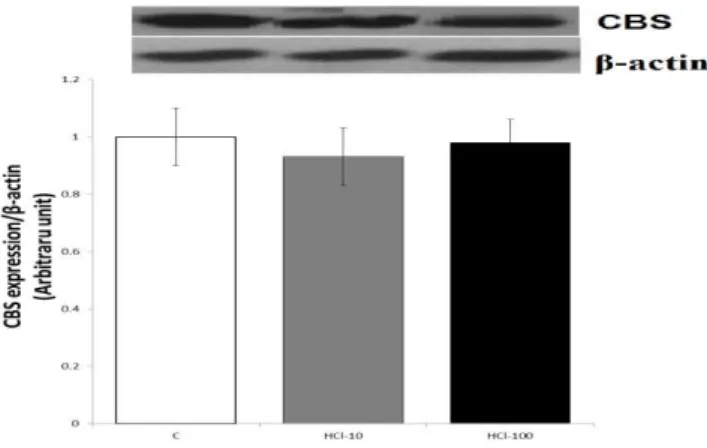
As illustrated in Figure 2, mucosal mRNA expression of CSE significantly increased in response to stimulated gastric acid secretion in normal rats (P<0.01), while the