Hypertrophy of NADH-diaphorase positive myenteric neurons in rat jejunum after acute infection caused by Toxoplasma gondii
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
4: histopathology in the brains of healthy mice, mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii and mice treated with Dialyzable leukocyte extracts from crocodile lymphoid tissue (DLEc)
This study aimed to assess the quantification and measurements of the cell body profile area (CBPA) of NADPH-diaphorase reactive (NADPH-dp) myenteric neurons of the jejunum of
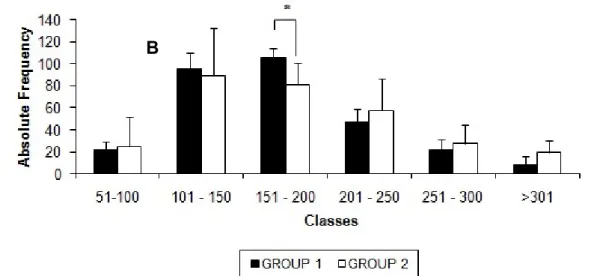
Frequency of myenteric neurons according to perikaryon to nucleus area ratio intervals of the control group (CG) and of birds inoculated with oocysts of Toxoplasma gondii strain
The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of the ascorbic acid supplementation in diabetic rats on the number and size of myenteric neurons NADH-diaphorase
Outcome of Toxoplasma gondii tissue cysts in commercial cuts of pork by mouse bioassay and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) obtained from infected pigs.. gondii of three
In the present study was demonstrated that the acute and chronic infection caused by genotype III tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii did not provoked alterations in the number
Three sets of possible predictors were considered: demographic variables (i.e., gender, age, and duration of sojourn), intercultural contact variables (i.e., Portuguese
Cumulative prevalence of acute toxoplasmosis infection in pregnant women according to ERNCT classification system and case definition of Toxoplasma gondii infection