Milk quality of Jersey cows kept on winter pasture supplemented or not with concentrate
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The higher leaf blade accumulation on the pasture kept at 15 cm in winter, as compared with pasture managed with an average height of 25 cm throughout the experimental
Both month and year are factors that interfere with total bacterial count, somatic cell count, and protein and fat of milk, and the best patterns are found in the coldest periods
The first one was used to determine total bacterial count (TBC) and somatic cell count (SCC) by flow cytometry and milk chemical composition (lactose, protein, fat, and total solids)
The effects of farm, parity (PO) and month of parturition on milk production, percentage of fat and protein, somatic cell count (SCC), and milk urea nitrogen (MUN) concentration
Traits related to milk quality (total solids) and udder health (somatic cell count) are important in dairy production.. In dairy goat production, milk quality has an essential
This study aimed at evaluating levels of concentrate supplementation on the production and quality of the milk, on intake and efficiency of nutrient use for milk production by
Mean rates for carcass and loin, fat thickness, weight of liver and weight of perirenal-pelvic fat of Nellore cows supplemented on pasture with and without the inclusion of
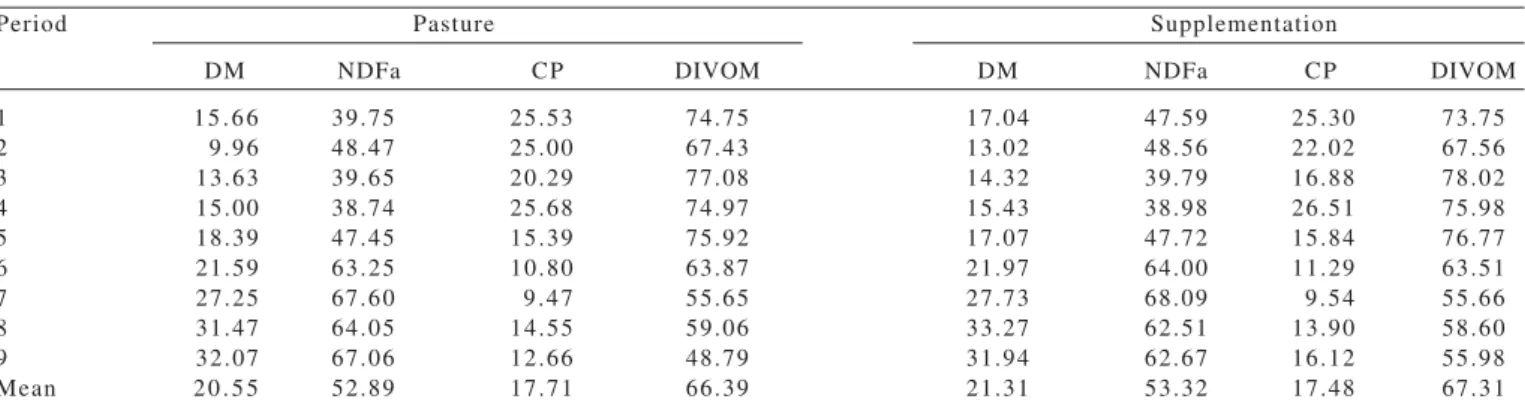
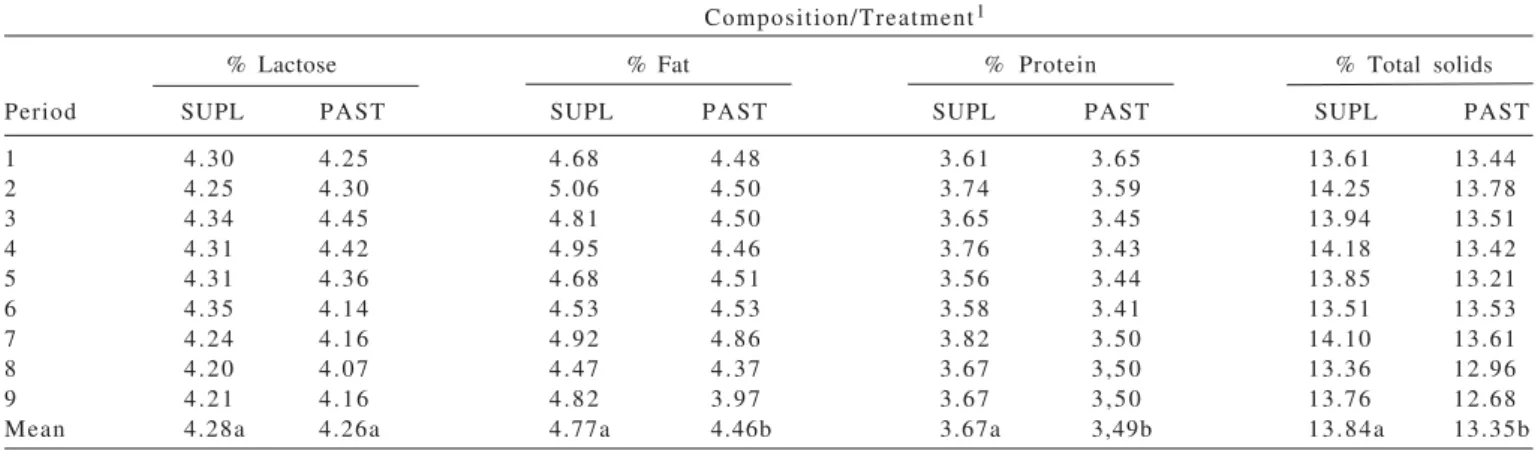
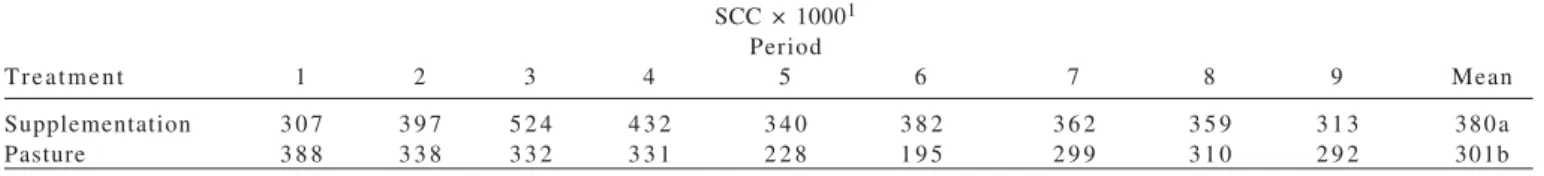
The dependent variables referring to the milk quality were percentages of fat, protein, lactose, total solids, and solids-not-fat, somatic cell count, and total bacterial count..