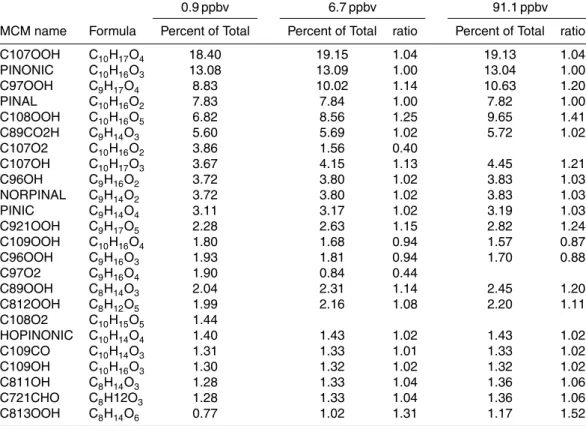
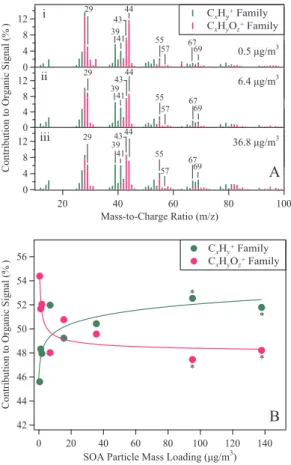
Loading-dependent elemental composition of α-pinene SOA particles
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
the mixing state of aerosol particles is classified as follows: if all particles of a cer- tain size have almost the same chemical composition, they are described as internally
Extended analysis of the chemical composition of sin- gle aerosol particles by a transmission electron microscope (TEM) coupled to an energy dispersive X-ray spectrome- ter
Secondary organic aerosols (SOA), formed by gas-to-particle conversion of oxidized vapors, and other oxygenated organic aerosols formed by chemical ageing of existing particles
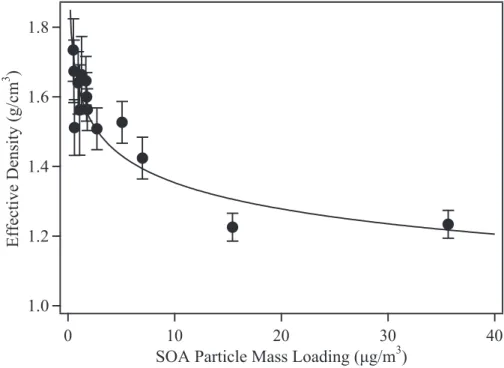
T.: Particle mass yield in secondary organic aerosol formed by the dark ozonolysis of alpha-pinene, Atmos. T.: Loading-dependent
At- mospheric simulation chambers are powerful tools to study the physical, chemical, optical and hygroscopic properties of SOA and follow their changes along their life cycle by
A wide range of smog chamber results obtained at various conditions (low/high NO x , presence/absence of UV radia- tion, dry/humid conditions, and temperatures ranging from 15–40 ◦
The effect of photochemical ageing and initial pre- cursor concentration on the composition and hygroscopic properties of secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formed dur- ing the
In an e ff ort to retrieve the m r s of SOA closely resembling ambient aerosol, this work explores the e ff ect of parent hydrocarbon ( α -pinene, limonene and toluene) and