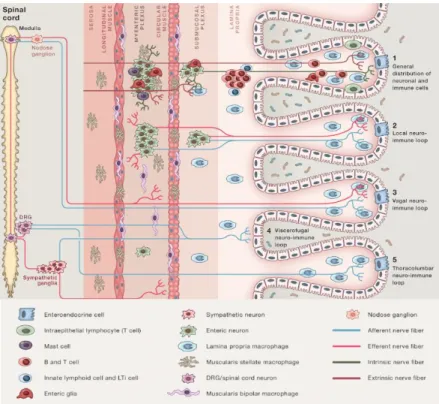
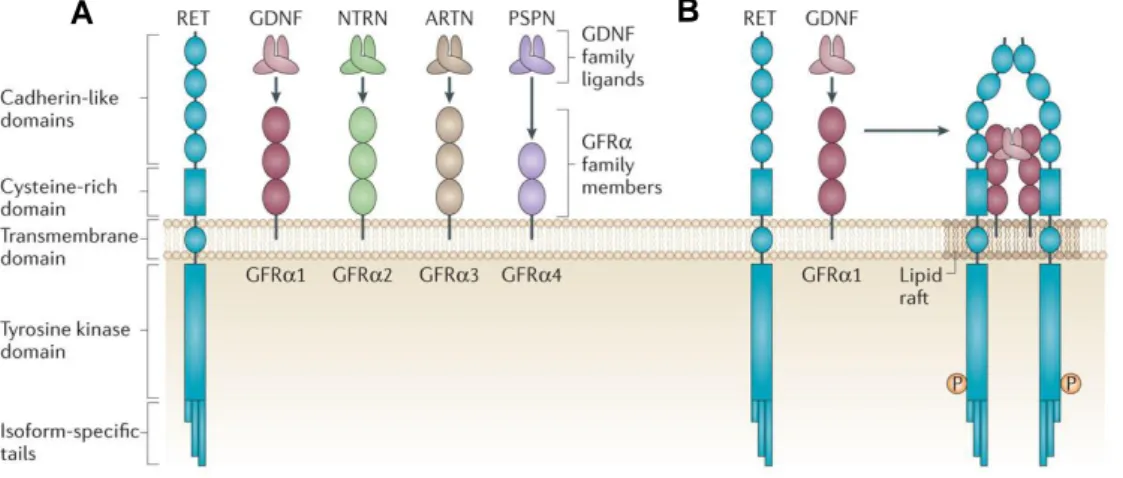
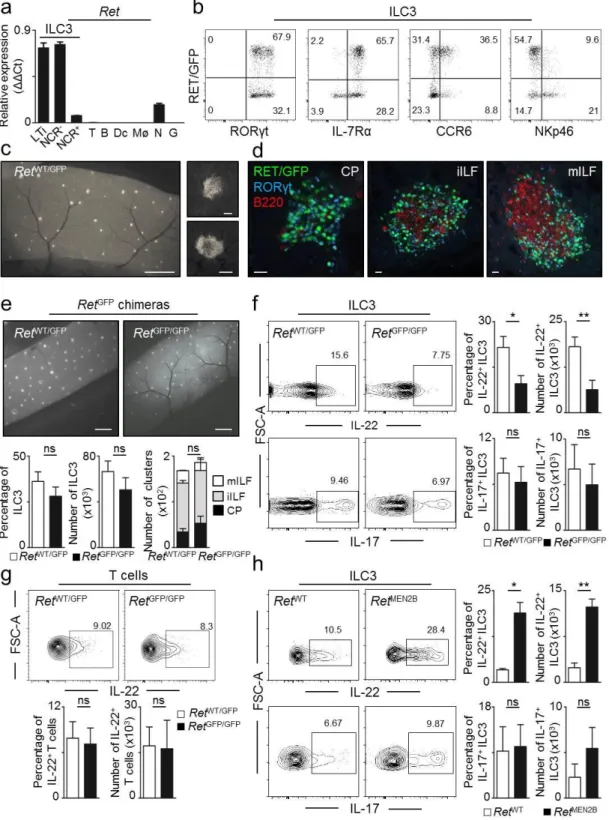
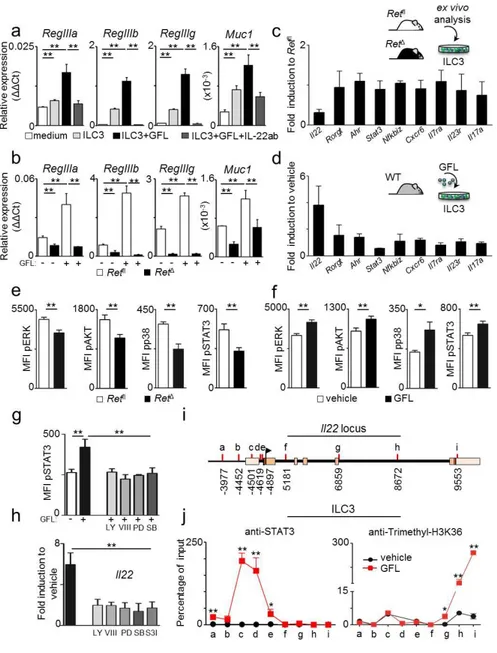
Glial cell-derived neuroregulators control type 3 innate lymphoid cells and gut defence
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Neuroprotection through delivery of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor by neural stem cells in a mouse model of Parkinson's
most abundant cell types are neurons, which are the brain function unit, and glial.. cells, which are responsible for a myriad of housekeeping,
É ainda de se destacar, no caso dos estudos realizados em dissertações de mestrado no contexto português, cada vez mais se tem vindo a procurar trabalhar
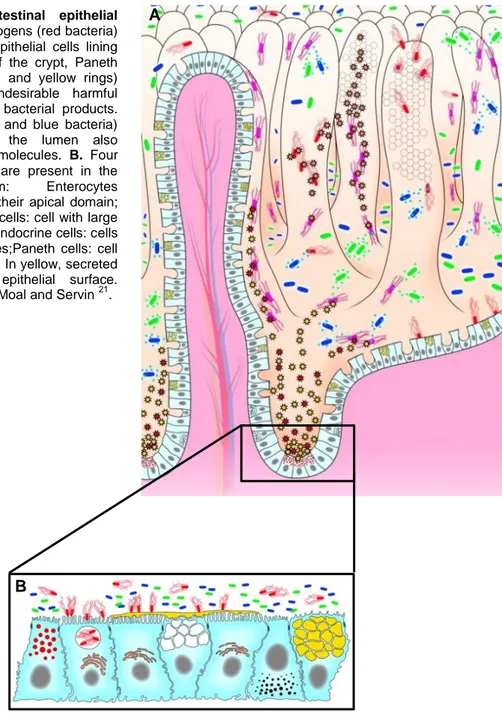
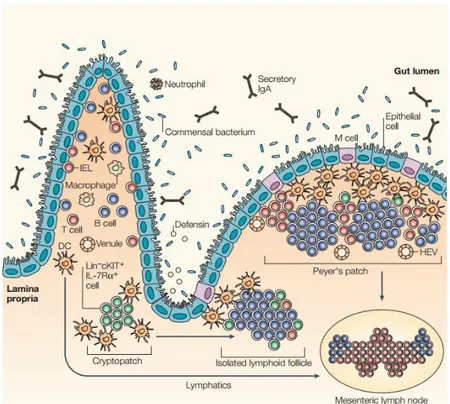
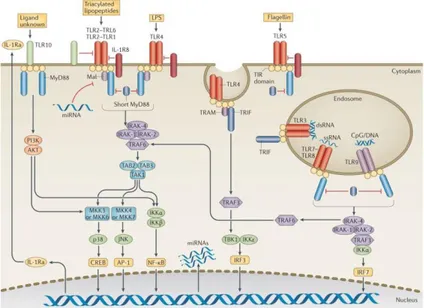
The recognition of bacterial components on the intestinal epithelial cells occurs through the toll like.. receptors and is followed by the induction of an effective
A, Semithin section of dorsal root ganglion showing the relationship between a large neuron (asterisk) and satellite glial cells.. The nuclei of a satellite glial cell is
Com tal proposição alcançada, mediante o estudo realizado, podemos afiançar considerações importantes dos dados investigados: a escola é um intenso movimento de assimilação
Objective: To correlate neurotrophic factors – brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line- derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and beta-nerve growth factor (beta-NGF)
Thus, intra–epithelial cell interactions are sufficient to limit collective cell migration in the absence of compensatory cell proliferation and can account for cell spacing and