Gender-Based Differences in Anxiety and Depression Following Acute Myocardial Infarction
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Como os pilares que suportam diretamente a laje foram considerados elementos secundários, os seus valores de momentos fletores e esforços transversos são nulos, assim,
Objective: The present study aimed to compare profiles and severity of carer burden, depression, anxiety and stress in carers of FTD patients in India in comparison to Australia;
The aim of this study was to evaluate left atrial dimensions and atrial natriuretic peptide levels in patients early after their first acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Objective: To investigate the prevalence of depression, anxiety, psychological stress, and Type D personality and its association with cardiovascular events in patients
Although the literature contains studies on the presence of anxiety and depression symptoms in the perioperative period of cardiac surgeries (6-7) , no stu- dies were found
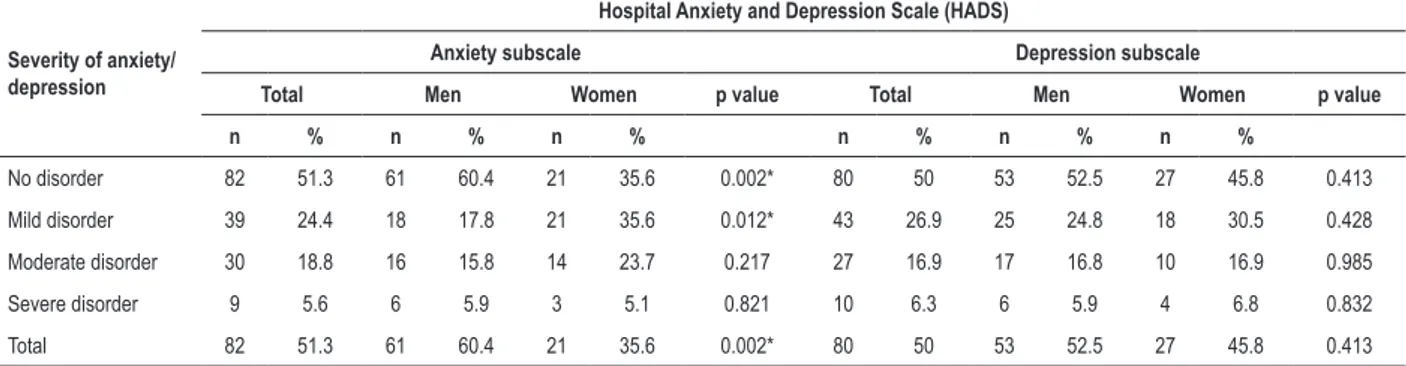
of anxiety and depression in patients after myocardial revascularization using the Hospital.. Anxiety and Depression
tive acute myocardial infarction in patients undergoing myocardial revascularization with saphenous vein bypass grafting, and showed that troponin I is an excellent marker to
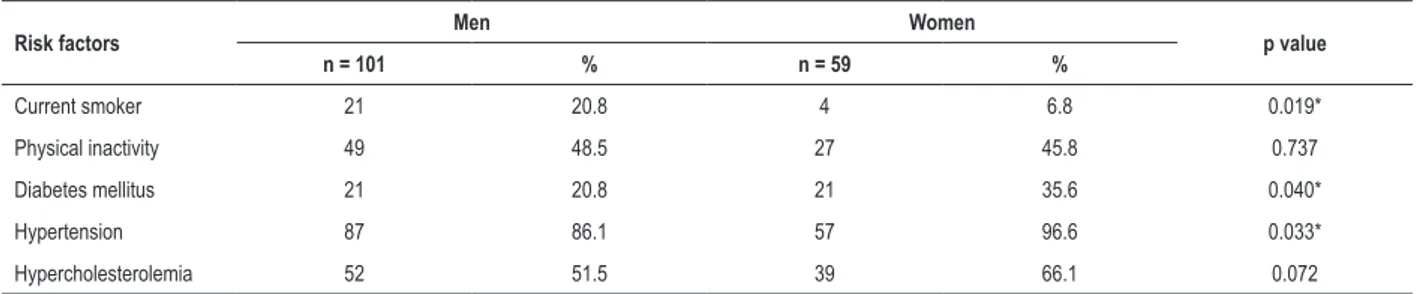
This study aimed at assessing the impact of smoking on in-hospital morbidity and mortality of patients experien- cing acute myocardial infarction and to assess the associa- tion