Determinants of optimal breast-feeding in peri-urban Guatemala City, Guatemala
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
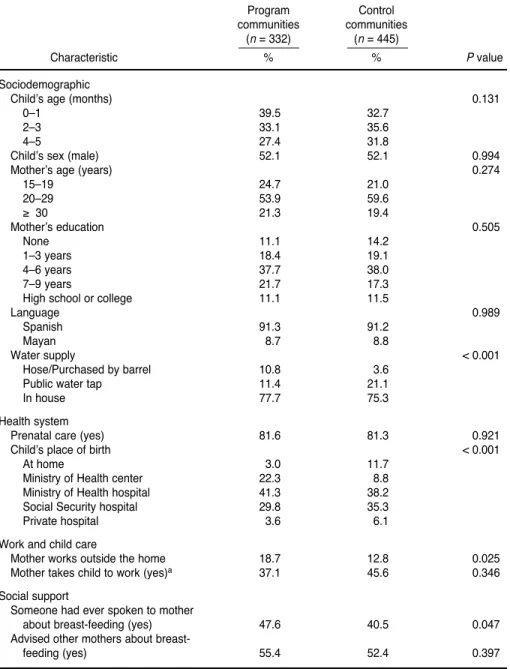
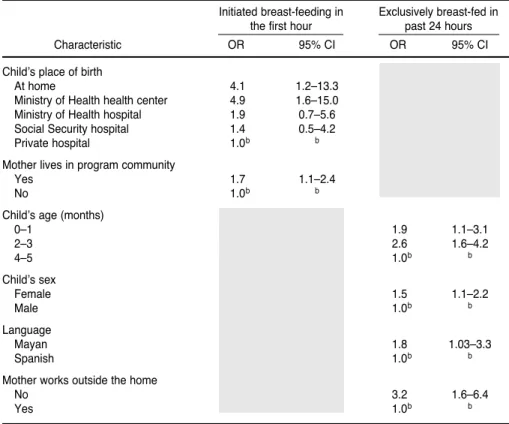
feeding: mother working outside the home, primiparity, low birth weight, child not breastfed within the irst hour, and child had consumed milk formula and tea on the irst day
It was revealed that wasting was associated with the neighborhood of residence, with the child ’ s age, parent ’ s age, if the father was living at home/ had another family, number
2-3 The objectives of the current study were to explore the relationship between breast feeding and diarrhea and to assess the effect of exclusive breast feeding
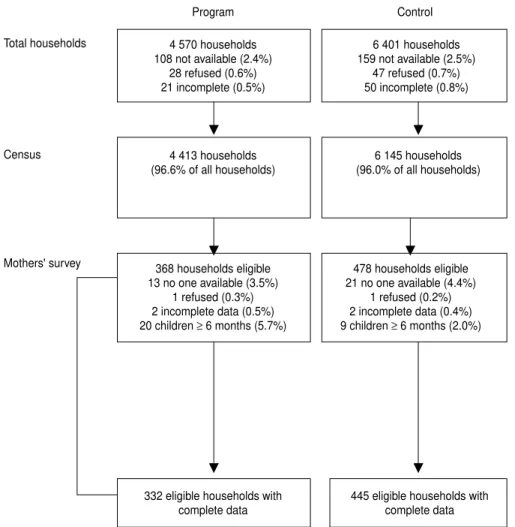
The interview served to identib the type offeeding (exclusive breast-feeding, breast-feeding plus bottle-feeding, breast-feeding plus solid food, exclusive bottlelfeeding,
7. Mental hygiene classes shall be included in the program to assist in protecting the child against mental and physical diseases. Mentally deficient children and those
The probability of attending school four our group of interest in this region increased by 6.5 percentage points after the expansion of the Bolsa Família program in 2007 and
Objective: The present study aimed to describe breast-feeding, complementary feeding and determining factors for early complementary feeding from birth to 8 months of age in a
total amount of breastfeeding time and low socioeconomic levels were associated with a higher risk of RWG, regardless of the age of the child, the age solid foods were introduced,