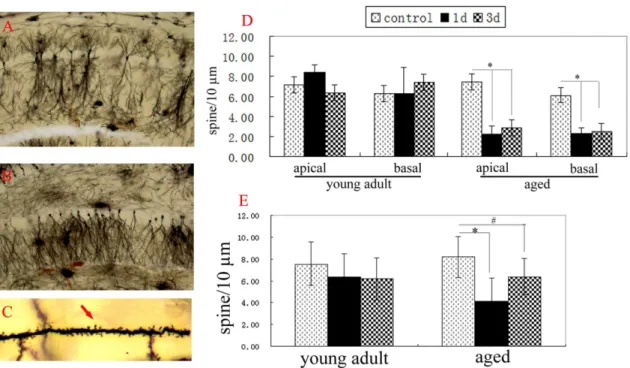
Aging differentially affects the loss of neuronal dendritic spine, neuroinflammation and memory impairment at rats after surgery.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
However, when ligature was placed, analysis revealed a significantly greater area of bone loss (p<0.05) in the furcation region of ligated teeth in rats that received high
Therefore, ischemic preconditioning was shown to be protective in bacterial translocation after ischemia and reperfusion in rats and the best result was found in the group with
The objective of this study was to evaluate liver regeneration after 60% partial hepatectomy in rats with and without action of diet supplemented with fatty acids evaluating
In the present study with female rats subjected to PPVL, the intact rats showed no signiicant increase in PP, but in the castrated rats PP was signiicantly increased (P<0.05)
In this study after a single systemic LPS injection the expression of TNF- a in the serum preceded the up-regulation of IL-1 b (Figure 1B) suggesting that activation of the
The rats were kept for 30 days; after this period, and with confirmation of the formation of the perianal fistula, the setons were introduced (10 rats – cotton thread #0; 10 rats
Nellis and Everard (1983) found that rats on a Caribbean island became primarily nocturnal and arboreal after the introduction of the mongoose. In sum, rats can become more
In conclusion, the same fluoride treatment scheme that caused memory impairment and dental fluorosis in rats (Chioca et al. 2007) was not able to demonstrate alterations on